Inhibition of the MAPK pathway alone is insufficient to account for all of the cytotoxic effects of naringenin in MCF-7 breast cancer cells
- PMID: 29450133
- PMCID: PMC5801822
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopen.2016.09.004
Inhibition of the MAPK pathway alone is insufficient to account for all of the cytotoxic effects of naringenin in MCF-7 breast cancer cells
Abstract
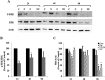
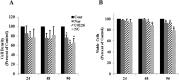
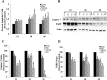
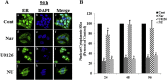
Estrogen receptor (ER) antagonists such as tamoxifen (Tam) have been used successfully to treat ER+ breast cancers for more than 30 years. Unfortunately, long term use of Tam can result in resistance. Tam resistance is associated with the activation of growth factor signaling pathways that promote cell proliferation and survival. The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), is up-regulated in Tam resistant (Tam-R) cells. Previous studies have reported that the flavanone, naringenin (Nar) can inhibit cell proliferation and induce apoptosis in ER+ breast cancer cells. Furthermore, Nar has been shown to inhibit the MAPK signaling pathways in MCF-7 cells. In this report we investigated whether inhibition of MAPK alone is mediating the effects of Nar on cell proliferation and viability. These studies will determine the mechanism of action of Nar. Tam-R MCF-7 breast cancer cells were treated with Nar or U0126, a MAPK kinase inhibitor. Our studies show that while both U0126 and Nar impaired cell proliferation and viability the combination of U0126 and Nar resulted in greater inhibition of cell viability than either compound alone. It has been previously reported that Nar can bind the ER. Our lab has also shown that Nar localizes ERα to a peri-nuclear region of the cell. Confocal microscopy revealed that in U0126 treated cells ERα displayed an even distribution across the cytoplasm as seen in untreated Tam-R cells. These studies suggest that MAPK is not the only target of Nar.
Keywords: MAPK signaling; Naringenin; Tamoxifen resistance.
Figures

References
-
- Sommer S., Fuqua S.A. Estrogen receptor and breast cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2001;11:339–352. - PubMed
-
- Clemons M., Danson S., Howell A. Tamoxifen (“Nolvadex”): a review. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2002;28:165–180. - PubMed
-
- Osborne C.K. Tamoxifen in the treatment of breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998;339:1609–1618. - PubMed
-
- Ali S., Coombes R.C. Endocrine-responsive breast cancer and strategies for combating resistance. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2002;2:101–112. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

