Human and mouse microarrays-guided expression analysis of membrane protein trafficking-related genes in MDCK cells, a canine epithelial model for apical and basolateral differential protein targeting
- PMID: 29450149
- PMCID: PMC5801818
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopen.2017.04.002
Human and mouse microarrays-guided expression analysis of membrane protein trafficking-related genes in MDCK cells, a canine epithelial model for apical and basolateral differential protein targeting
Abstract
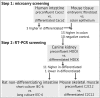
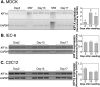
MDCK cells are widely used to study the differential targeting of membrane transporters to apical and basolateral membrane but its canine origin limited the commercial tools available for the analysis of protein trafficking machinery. Because apical and basolateral membranes are only found in differentiated epithelial cells, genes critical for differential targeting may be specifically up-regulated upon MDCK cell differentiation. To search for these genes, a cross-species screening strategy was used. We first analyzed the human microarray data for protein trafficking-related genes that were up-regulated in colon carcinoma Caco2 cells upon differentiation. The results of mouse 44K gene expression microarray analysis were then used to extract additional candidate genes that showed higher expression in normal colon epithelium compared to primary embryonic fibroblasts. Finally, NCBI genomic sequence information was used to design RT-PCR primers for 13 candidate and 10 negative control genes and used to analyze MDCK cells at 2, 13 and 17 days after seeding. To determine whether the gene up-regulation was specific in epithelial differentiation, we also performed RT-PCR on rat non-differentiating intestinal IEC-6 cells and mouse C2C12 cells, a differentiating myoblast model. Of the 13 candidate genes, 3 genes, SDCBP2, KIF12, KIF27, met all criteria of specific up-regulation in differentiated MDCK cells. In addition, KIF13A showed up-regulation in differentiated MDCK and C2C12 cells but not in IEC-6 cells cultured for the same duration. The functions of these genes need to be analyzed in the future. This cross-species screening strategy may be useful for other non-human, non-rodent cell models.
Keywords: Differentiation; Epithelium; Kinesin; MDCK cells; RAB; SDCBP2.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of the transfected Na+/H+-exchanger NHE3 in MDCK cells by vasotocin.Pflugers Arch. 1997 May;434(1):123-31. doi: 10.1007/s004240050372. Pflugers Arch. 1997. PMID: 9094265
-
Cytoplasmic juxtamembrane domain of the human EGF receptor is required for basolateral localization in MDCK cells.J Cell Physiol. 1995 Mar;162(3):434-46. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041620316. J Cell Physiol. 1995. PMID: 7860650
-
Selective alterations in biosynthetic and endocytic protein traffic in Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial cells expressing mutants of the small GTPase Rac1.Mol Biol Cell. 2000 Jan;11(1):287-304. doi: 10.1091/mbc.11.1.287. Mol Biol Cell. 2000. PMID: 10637309 Free PMC article.
-
Apical and basolateral coated pits of MDCK cells differ in their rates of maturation into coated vesicles, but not in the ability to distinguish between mutant hemagglutinin proteins with different internalization signals.J Cell Biol. 1995 Jun;129(5):1241-50. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.5.1241. J Cell Biol. 1995. PMID: 7775571 Free PMC article.
-
SNARE protein trafficking in polarized MDCK cells.Traffic. 2000 Jul;1(7):553-60. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0854.2000.010705.x. Traffic. 2000. PMID: 11208143
Cited by
-
Lnc-EPB41-Protein Interactions Associated with Congenital Pouch Colon.Biomolecules. 2018 Sep 17;8(3):95. doi: 10.3390/biom8030095. Biomolecules. 2018. PMID: 30227690 Free PMC article.
-
Partial deletion of chromosome 6p causing developmental delay and mild dysmorphisms in a child: molecular and developmental investigation and literature search.Mol Cytogenet. 2021 Jul 24;14(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s13039-021-00557-y. Mol Cytogenet. 2021. PMID: 34303382 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marchiando A., Graham W., Turner J. Epithelial barriers in homeostasis and disease. Ann. Rev. Pathol. 2010;5:119–144. - PubMed
-
- Ullrich K., Frömter E., Murer H. Principles of epithelial transport in the kidney and intestines. Klin. Wochenschr. 1979;57:977–991. - PubMed
-
- Verrey F., Ristic Z., Romeo E., Ramadan T., Makrides V., Dave M., Wagner C., Camargo S. Novel renal amino acid transporters. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2005;67:557–572. - PubMed
-
- Takano M., Yumoto R., Murakami T. Expression and function of efflux drug transporters in the intestine. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006;109:137–161. - PubMed
-
- Regårdh C. Factors contributing to variability in drug pharmacokinetics. IV. Renal excretion. J. Clin. Hosp. Pharm. 1985;10:337–349. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

