Unilateral Eales' disease a case report
- PMID: 29450389
- PMCID: PMC5710024
- DOI: 10.22336/rjo.2017.27
Unilateral Eales' disease a case report
Abstract
Introduction. Eales disease is an idiopathic peripheral vascular occlusive disease characterized by inflammation, ischemia, and retinal neovascularization and is hallmarked by recurrent vitreous hemorrhages and vision loss. Case report. We present a case of a 48-year-old female with recurrent floaters and decreased vision in her right eye. The onset of symptoms was in 2007 when a diagnose of retinal vasculitis was made. She had no accompanying systemic signs and symptoms and no history of ocular trauma or previous tuberculosis infection. The eye condition was managed only with intermittent focal laser treatment, because the general treatment with steroids was not efficient and poorly tolerated. After the laser treatment, the visual acuity completely recovered and there was no recurrence of vitreous hemorrhage. The case particularity was the unilaterality after 9 years from the onset.
Keywords: Eales; focal laser; recurrent floaters.
Figures
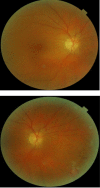
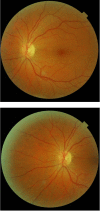

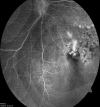

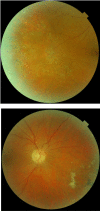
References
-
- Yannuzzi LA. The Retinal Atlas. Retinal Vascular Diseases, Eales’ Disease. Elsevier; 2010. pp. 433–438.
-
- Mwndoza KA, Lauer A. Eales Disease. American Academy of Ophthalmology. 2015 http://eyewiki.org/Eales_Disease.
-
- Kanski JJ, Bowling B. Clinical Ophthalmology a systematic approach. Eales Disease. Seventh edition. Elsevier; 2011. pp. 583–586.
-
- Nussenblatt RB, Whitcup SM. Uveitis: Fundamentals and Clinical Practice. Eales’ Disease. Fourth Edition. Elsevier; 2010. pp. 356–359.
-
- Garg SJ. Color Atlas & Synopsis of Clinical Ophthalmology Wills Eye Institute. Uveitis; Eales’ Disease. 2012:101–103.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
