Sarcopenia and risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 29451179
- PMCID: PMC5848318
- DOI: 10.4103/sjg.SJG_237_17
Sarcopenia and risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Background/aim: The association between sarcopenia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has been suggested by recent epidemiological studies, although the results have been inconsistent. This meta-analysis was conducted to summarize all available data and estimate the risk of NAFLD among patients with sarcopenia.
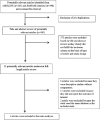
Materials and methods: A comprehensive literature review was conducted using MEDLINE and EMBASE databases through November 2016 to identify all studies that compared the risk of NAFLD among patients with sarcopenia versus those without sarcopenia. Effect estimates from each study were extracted and combined using the random-effect, generic inverse variance method of DerSimonian and Laird.
Results: Five cross-sectional studies with 27,804 participants met the eligibility criteria and were included in the meta-analysis. The risk of NAFLD in patients with sarcopenia was significantly higher than those without sarcopenia with the pooled odds ratio of 1.54 (95% confidence interval, 1.05-2.26). The statistical heterogeneity was high with an I2of 83%.
Conclusions: A significantly increased risk of NAFLD among patients with sarcopenia was observed in this study.
Keywords: Low muscle mass; meta-analysis; nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; sarcopenia.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between gastroesophageal reflux disease and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis.Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2017 Nov-Dec;23(6):311-317. doi: 10.4103/sjg.SJG_161_17. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 29205182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Urolithiasis. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2018 Dec;27(4):427-432. doi: 10.15403/jgld.2014.1121.274.nac. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2018. PMID: 30574625
-
Hyperuricaemia and risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis.Liver Int. 2017 Jun;37(6):906-918. doi: 10.1111/liv.13329. Epub 2016 Dec 31. Liver Int. 2017. PMID: 27891768 Review.
-
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 May;32(5):601-608. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001541. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 31567712
-
The association between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and atrial fibrillation: A meta-analysis.Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2017 Oct;41(5):525-532. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2017.08.001. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28866089 Review.
Cited by
-
Disease-Related Malnutrition and Sarcopenia as Determinants of Clinical Outcome.Visc Med. 2019 Oct;35(5):282-291. doi: 10.1159/000502867. Epub 2019 Sep 2. Visc Med. 2019. PMID: 31768391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between the risk of malnutrition and sarcopenia at 4.2 years of follow-up in community-dwelling older adults.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Feb 26;11:1363977. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1363977. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38476442 Free PMC article.
-
Change in skeletal muscle mass is associated with hepatic steatosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Sci Rep. 2023 Apr 28;13(1):6920. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-34263-z. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37117864 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of sarcopenia and physical inactivity to mortality in people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.JHEP Rep. 2020 Aug 15;2(6):100171. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2020.100171. eCollection 2020 Dec. JHEP Rep. 2020. PMID: 32964202 Free PMC article.
-
Fatty liver disease in children (MAFLD/PeFLD Type 2): unique classification considerations and challenges.Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2023 Mar 22;14:20420188231160388. doi: 10.1177/20420188231160388. eCollection 2023. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2023. PMID: 36968656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Janssen I. The epidemiology of sarcopenia. Clin Geriatr Med. 2011;27:355–63. - PubMed
-
- Baumgartner RN, Waters DL, Gallagher D, Morley JE, Garry PJ. Predictors of skeletal muscle mass in elderly men and women. Mech Ageing Dev. 1999;107:123–36. - PubMed
-
- Lindle RS, Metter EJ, Lynch NA, Fleg JL, Fozard JL, Tobin J, et al. Age and gender comparisons of muscle strength in 654 women and men aged 20-93 yr. J Appl Physiol. 1997;83:1581–7. - PubMed
-
- Janssen I. Influence of sarcopenia on the development of physical disability: The Cardiovascular Health Study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006;54:56–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous