Electroacupuncture preconditioning protects against focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via suppression of dynamin-related protein 1
- PMID: 29451211
- PMCID: PMC5840997
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.224373
Electroacupuncture preconditioning protects against focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via suppression of dynamin-related protein 1
Abstract
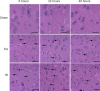
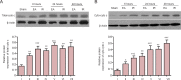
Electroacupuncture preconditioning at acupoint Baihui (GV20) can reduce focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. However, the precise protective mechanism remains unknown. Mitochondrial fission mediated by dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1) can trigger neuronal apoptosis following cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Herein, we examined the hypothesis that electroacupuncture pretreatment can regulate Drp1, and thus inhibit mitochondrial fission to provide cerebral protection. Rat models of focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury were established by middle cerebral artery occlusion at 24 hours after 5 consecutive days of preconditioning with electroacupuncture at GV20 (depth 2 mm, intensity 1 mA, frequency 2/15 Hz, for 30 minutes, once a day). Neurological function was assessed using the Longa neurological deficit score. Pathological changes in the ischemic penumbra on the injury side were assessed by hematoxylin-eosin staining. Cellular apoptosis in the ischemic penumbra on the injury side was assessed by terminal deoxyribonucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP-digoxigenin nick end labeling staining. Mitochondrial ultrastructure in the ischemic penumbra on the injury side was assessed by transmission electron microscopy. Drp1 and cytochrome c expression in the ischemic penumbra on the injury side were assessed by western blot assay. Results showed that electroacupuncture preconditioning decreased expression of total and mitochondrial Drp1, decreased expression of total and cytosolic cytochrome c, maintained mitochondrial morphology and reduced the proportion of apoptotic cells in the ischemic penumbra on the injury side, with associated improvements in neurological function. These data suggest that electroacupuncture preconditioning-induced neuronal protection involves inhibition of the expression and translocation of Drp1.
Keywords: apoptosis; cytochrome c; death-associated protein kinases; dynamin-related protein 1; electroacupuncture; focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury; mitochondrial dynamics; mitochondrial ultrastructure; nerve regeneration; neural regeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Autophagy: novel insights into therapeutic target of electroacupuncture against cerebral ischemia/ reperfusion injury.Neural Regen Res. 2019 Jun;14(6):954-961. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.250569. Neural Regen Res. 2019. PMID: 30761999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electroacupuncture protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through mitochondrial dynamics.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 19;10(14):e34986. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34986. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39148973 Free PMC article.
-
Selective cerebral hypothermia alleviates focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via enhancing SUMO2/3 modification of Drp1 in rats.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2025 May;182-183:106772. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2025.106772. Epub 2025 Mar 21. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2025. PMID: 40122332
-
Hypothermia-induced ischemic tolerance is associated with Drp1 inhibition in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury of mice.Brain Res. 2016 Sep 1;1646:73-83. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2016.05.042. Epub 2016 May 26. Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 27235868
-
Neuroprotective effects of electroacupuncture in ischemic stroke: from mechanisms to clinical implications.Front Aging Neurosci. 2025 Apr 24;17:1562925. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1562925. eCollection 2025. Front Aging Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40353059 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Electroacupuncture Pretreatment against Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury through Mitophagy.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Sep 9;2020:7486041. doi: 10.1155/2020/7486041. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32963572 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy: novel insights into therapeutic target of electroacupuncture against cerebral ischemia/ reperfusion injury.Neural Regen Res. 2019 Jun;14(6):954-961. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.250569. Neural Regen Res. 2019. PMID: 30761999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial Transplantation Attenuates Neural Damage and Improves Locomotor Function After Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury in Rats.Front Neurosci. 2022 Apr 12;16:800883. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.800883. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35495036 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese medicine in treating ischemic stroke by modulating mitochondria: A comprehensive overview of experimental studies.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 22;14:1138128. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1138128. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37033646 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective brain hypothermia-induced neuroprotection against focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury is associated with Fis1 inhibition.Neural Regen Res. 2020 May;15(5):903-911. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.268973. Neural Regen Res. 2020. PMID: 31719256 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atkins K, Dasgupta A, Chen KH, Mewburn J, Archer SL. The role of Drp1 adaptor proteins MiD49 and MiD51 in mitochondrial fission: implications for human disease. Clin Sci (Lond) 2016;130:1861–1874. - PubMed
-
- Cheng CY, Lin JG, Su SY, Tang NY, Kao ST, Hsieh CL. Electroacupuncture-like stimulation at Baihui and Dazhui acupoints exerts neuroprotective effects through activation of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor-mediated MEK1/2/ERK1/2/p90RSK/bad signaling pathway in mild transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014b;14:92. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

