An Indispensable Role of Androgen Receptor in Wnt Responsive Cells During Prostate Development, Maturation, and Regeneration
- PMID: 29451339
- PMCID: PMC5992030
- DOI: 10.1002/stem.2806
An Indispensable Role of Androgen Receptor in Wnt Responsive Cells During Prostate Development, Maturation, and Regeneration
Abstract
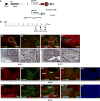
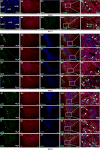
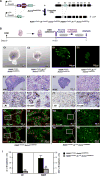
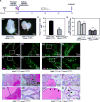
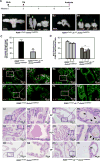
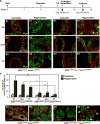
Androgen signaling is essential for prostate development, morphogenesis, and regeneration. Emerging evidence indicates that Wnt/β-catenin signaling also contributes to prostate development specifically through regulation of cell fate determination. Prostatic Axin2-expressing cells are able to respond to Wnt signals and possess the progenitor properties to regenerate prostatic epithelium. Despite critical roles of both signaling pathways, the biological significance of androgen receptor (AR) in Axin2-expressing/Wnt-responsive cells remains largely unexplored. In this study, we investigated this important question using a series of newly generated mouse models. Deletion of Ar in embryonic Axin2-expressing cells impaired early prostate development in both ex vivo and tissue implantation experiments. When Ar expression was deleted in prostatic Axin2-expressing cells at pre-puberty stages, it results in smaller and underdeveloped prostates. A subpopulation of Axin2 expressing cells in prostate epithelium is resistant to castration and, following androgen supplementation, is capable to expand to prostatic luminal cells. Deletion of Ar in these Axin2-expressing cells reduces their regenerative ability. These lines of evidence demonstrate an indispensable role for the Ar in Wnt-responsive cells during the course of prostate development, morphogenesis, and regeneration, which also imply an underlying interaction between the androgen and Wnt signaling pathways in the mouse prostate. Stem Cells 2018;36:891-902.
Keywords: Androgen receptor; Prostate development; Wnt signaling; β-Catenin.
© 2018 The Authors STEM CELLS published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of AlphaMed Press.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Balk SP. Androgen receptor as a target in androgen-independent prostate cancer. Urology. 2002;60:132–138. discussion 138-139. - PubMed
-
- Gelmann EP. Molecular biology of the androgen receptor. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:3001–3015. - PubMed
-
- Zhou ZX, Wong CI, Sar M, et al. The androgen receptor: an overview. Recent Progress Hormone Research. 1994;49:249–274. - PubMed
-
- Cunha GR, Donjacour AA, Cooke PS, et al. The endocrinology and developmental biology of the prostate. Endocr Rev. 1987;8:338–362. - PubMed
-
- Sugimura Y, Cunha GR, Donjacour AA. Morphogenesis of ductal networks in the mouse prostate. Biol Reprod. 1986;34:961–971. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

