Reporting of sex and gender in randomized controlled trials in Canada: a cross-sectional methods study
- PMID: 29451565
- PMCID: PMC5803639
- DOI: 10.1186/s41073-017-0039-6
Reporting of sex and gender in randomized controlled trials in Canada: a cross-sectional methods study
Abstract
Background: Accurate reporting on sex and gender in health research is integral to ensuring that health interventions are safe and effective. In Canada and internationally, governments, research organizations, journal editors, and health agencies have called for more inclusive research, provision of sex-disaggregated data, and the integration of sex and gender analysis throughout the research process. Sex and gender analysis is generally defined as an approach for considering how and why different subpopulations (e.g., of diverse genders, ages, and social locations) may experience health conditions and interventions in different or similar ways.The objective of this study was to assess the extent and nature of reporting about sex and/or gender, including whether sex and gender analysis (SGA) was carried out in a sample of Canadian randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with human participants.
Methods: We searched MEDLINE from 01 January 2013 to 23 July 2014 using a validated filter for identification of RCTs, combined with terms related to Canada. Two reviewers screened the search results to identify the first 100 RCTs that were either identified in the trial publication as funded by a Canadian organization or which had a first or last author based in Canada. Data were independently extracted by two people from 10% of the RCTs during an initial training period; once agreement was reached on this sample, the remainder of the data extraction was completed by one person and verified by a second.
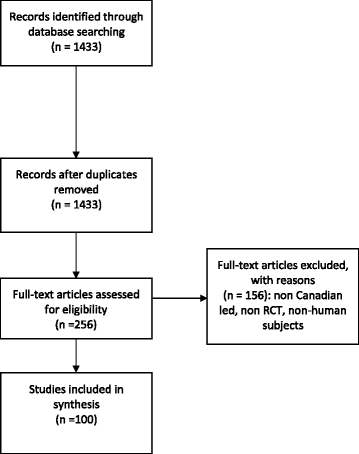
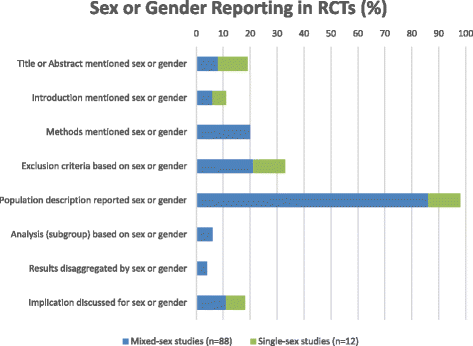
Results: The search yielded 1433 records. We screened 256 records to identify 100 RCTs which met our eligibility criteria. The median sample size of the RCTs was 107 participants (range 12-6085). While 98% of studies described the demographic composition of their participants by sex, only 6% conducted a subgroup analysis across sex and 4% reported sex-disaggregated data. No article defined "sex" and/or "gender." No publication carried out a comprehensive sex and gender analysis.
Conclusions: Findings highlight poor uptake of sex and gender considerations in the Canadian RCT context and underscore the need for better articulated guidance on sex and gender analysis to improve reporting of evidence, inform policy development, and guide future research.
Keywords: Canada; Gender; Quality; Randomized controlled trials as a topic; Sex/gender analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Not applicable.Not applicable.The authors declare that they have no competing interests.Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
Recovery schools for improving behavioral and academic outcomes among students in recovery from substance use disorders: a systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2018 Oct 4;14(1):1-86. doi: 10.4073/csr.2018.9. eCollection 2018. Campbell Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 37131375 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioural interventions for type 2 diabetes: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2009;9(21):1-45. Epub 2009 Oct 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2009. PMID: 23074526 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic reviews of the effectiveness of day care for people with severe mental disorders: (1) acute day hospital versus admission; (2) vocational rehabilitation; (3) day hospital versus outpatient care.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(21):1-75. doi: 10.3310/hta5210. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532238 Review.
-
Convalescent plasma or hyperimmune immunoglobulin for people with COVID-19: a living systematic review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 May 20;5(5):CD013600. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013600.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Feb 1;2:CD013600. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013600.pub5. PMID: 34013969 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
The gender and geography of publishing: a review of sex/gender reporting and author representation in leading general medical and global health journals.BMJ Glob Health. 2021 May;6(5):e005672. doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2021-005672. BMJ Glob Health. 2021. PMID: 33986001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Patient engagement partnerships in clinical trials (PEP-CT): protocol for the systematic development and testing of patient partner and investigator decision aids.BMJ Open. 2022 Feb 21;12(2):e060267. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-060267. BMJ Open. 2022. PMID: 35190448 Free PMC article.
-
Sex and gender-based analysis and diversity metric reporting in acute care trials published in high-impact journals: a systematic review.BMJ Open. 2024 May 7;14(5):e081118. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-081118. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 38719297 Free PMC article.
-
Sex- and Gender-Based Analysis in Cannabis Treatment Outcomes: A Systematic Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Jan 30;17(3):872. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17030872. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32019247 Free PMC article.
-
Considerations of sex and gender dimensions by research ethics committees: a scoping review.Int Health. 2022 Nov 1;14(6):554-561. doi: 10.1093/inthealth/ihab093. Int Health. 2022. PMID: 35043198 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Doull M, Welch V, Puil L, Runnels V, Coen SE, Shea B, O'Neill J, Borkhoff C, Tudiver S, Boscoe M. Development and evaluation of ‘briefing notes’ as a novel knowledge translation tool to aid the implementation of sex/gender analysis in systematic reviews: a pilot study. PLoS One. 2014;9(11):e110786. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110786. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous