Mechanisms of imidazoline I2 receptor agonist-induced antinociception in rats: involvement of monoaminergic neurotransmission
- PMID: 29451703
- PMCID: PMC5900992
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.14161
Mechanisms of imidazoline I2 receptor agonist-induced antinociception in rats: involvement of monoaminergic neurotransmission
Abstract
Background and purpose: Although the antinociceptive efficacies of imidazoline I2 receptor agonists have been established, the exact post-receptor mechanisms remain unknown. This study tested the hypothesis that monoaminergic transmission is critical for I2 receptor agonist-induced antinociception.
Experimental approach: von Frey filaments were used to assess antinociceptive effects of two I2 receptor agonists, 2-BFI and CR4056 on chronic constriction injury (CCI)-induced neuropathic pain or complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA)-induced inflammatory pain in rats. Rectal temperature was measured to assess hypothermic effects of 2-BFI. A two-lever drug discrimination paradigm in which rats were trained to discriminate 5.6 mg·kg-1 2-BFI (i.p.) from its vehicle was used to examine the discriminative stimulus effects of 2-BFI. In each experiment, pharmacological mechanisms were investigated by combining 2-BFI or CR4056 with various pharmacological manipulations of the monoaminergic system including selective reuptake inhibition, monoamine depletion and monoamine receptor antagonism.
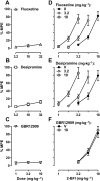
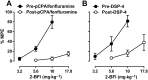
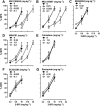
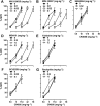
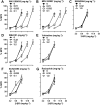
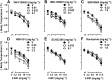
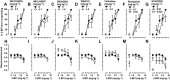
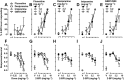
Key results: In the CCI model, selective reuptake inhibitors of 5-HT (fluoxetine) or noradrenaline (desipramine), but not dopamine (GBR12909), enhanced 2-BFI-induced antinociception. Selective depletion of 5-HT or noradrenaline almost abolished 2-BFI-induced antinociception. 5-HT1A , 5-HT2A and α1 -adrenoceptor antagonists, but not other monoaminergic antagonists, attenuated 2-BFI and CR4056-induced antinociception in CCI and/or CFA models. However, none of these monoamine receptor antagonists significantly altered 2-BFI-induced hypothermia or discriminative stimulus effects.
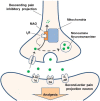
Conclusions and implications: Antinociception induced by I2 receptor agonists was mediated by serotonergic and noradrenergic mechanisms with 5-HT1A , 5-HT2A and α1 -adrenoceptor being particularly important. In contrast, the hypothermic and discriminative stimulus effects of I2 receptor agonists were mediated by distinct, independent mechanisms.
© 2018 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of intracellular Ca2+ signaling in the antinociceptive and discriminative stimulus effects of the imidazoline I2 receptor agonist 2-BFI in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017 Nov;234(22):3299-3307. doi: 10.1007/s00213-017-4719-1. Epub 2017 Aug 19. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28825118 Free PMC article.
-
Potential serotonergic and noradrenergic involvement in the discriminative stimulus effects of the selective imidazoline I2-site ligand 2-BFI.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2003 May;75(2):427-33. doi: 10.1016/s0091-3057(03)00136-9. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2003. PMID: 12873635
-
Antinociceptive effects of imidazoline I2 receptor agonists in the formalin test in rats.Behav Pharmacol. 2016 Jun;27(4):377-83. doi: 10.1097/FBP.0000000000000206. Behav Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26599907 Free PMC article.
-
Imidazoline I2 receptors: An update.Pharmacol Ther. 2017 Oct;178:48-56. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.03.009. Epub 2017 Mar 16. Pharmacol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28322973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New approaches to developing antidepressants by enhancing monoaminergic neurotransmission.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2003 Apr;12(4):531-43. doi: 10.1517/13543784.12.4.531. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2003. PMID: 12665410 Review.
Cited by
-
The imidazoline I2 receptor agonist 2-BFI reduces abuse-related effects of morphine: self-administration and drug discrimination.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2024 Mar;241(3):479-487. doi: 10.1007/s00213-023-06524-2. Epub 2023 Dec 30. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2024. PMID: 38159161 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of imidazoline I2 receptor agonists on reserpine-induced hyperalgesia and depressive-like behavior in rats.Behav Pharmacol. 2019 Aug;30(5):429-434. doi: 10.1097/FBP.0000000000000454. Behav Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30383551 Free PMC article.
-
An excitatory lateral hypothalamic circuit orchestrating pain behaviors in mice.Elife. 2021 May 27;10:e66446. doi: 10.7554/eLife.66446. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34042586 Free PMC article.
-
High plasma levels of pro-inflammatory factors interleukin-17 and interleukin-23 are associated with poor outcome of cardiac-arrest patients: a single center experience.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020 Apr 15;20(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s12872-020-01451-y. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020. PMID: 32293300 Free PMC article.
-
Improved efficacy, tolerance, safety, and abuse liability profile of the combination of CR4056 and morphine over morphine alone in rodent models.Br J Pharmacol. 2020 Jul;177(14):3291-3308. doi: 10.1111/bph.15049. Epub 2020 Apr 24. Br J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32154915 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Research Council (2011). Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. edn, 10.17226/12910. National Academy of Sciences: Washington DC.
-
- Bardin L (2011). The complex role of serotonin and 5‐HT receptors in chronic pain. Behav Pharmacol 22: 390–404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

