Mechanisms of imidazoline I2 receptor agonist-induced antinociception in rats: involvement of monoaminergic neurotransmission
- PMID: 29451703
- PMCID: PMC5900992
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.14161
Mechanisms of imidazoline I2 receptor agonist-induced antinociception in rats: involvement of monoaminergic neurotransmission
Abstract
Background and purpose: Although the antinociceptive efficacies of imidazoline I2 receptor agonists have been established, the exact post-receptor mechanisms remain unknown. This study tested the hypothesis that monoaminergic transmission is critical for I2 receptor agonist-induced antinociception.
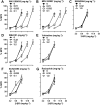
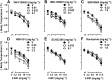
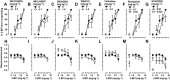
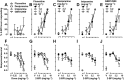
Experimental approach: von Frey filaments were used to assess antinociceptive effects of two I2 receptor agonists, 2-BFI and CR4056 on chronic constriction injury (CCI)-induced neuropathic pain or complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA)-induced inflammatory pain in rats. Rectal temperature was measured to assess hypothermic effects of 2-BFI. A two-lever drug discrimination paradigm in which rats were trained to discriminate 5.6 mg·kg-1 2-BFI (i.p.) from its vehicle was used to examine the discriminative stimulus effects of 2-BFI. In each experiment, pharmacological mechanisms were investigated by combining 2-BFI or CR4056 with various pharmacological manipulations of the monoaminergic system including selective reuptake inhibition, monoamine depletion and monoamine receptor antagonism.
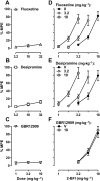
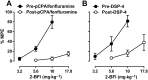
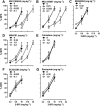
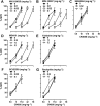
Key results: In the CCI model, selective reuptake inhibitors of 5-HT (fluoxetine) or noradrenaline (desipramine), but not dopamine (GBR12909), enhanced 2-BFI-induced antinociception. Selective depletion of 5-HT or noradrenaline almost abolished 2-BFI-induced antinociception. 5-HT1A , 5-HT2A and α1 -adrenoceptor antagonists, but not other monoaminergic antagonists, attenuated 2-BFI and CR4056-induced antinociception in CCI and/or CFA models. However, none of these monoamine receptor antagonists significantly altered 2-BFI-induced hypothermia or discriminative stimulus effects.
Conclusions and implications: Antinociception induced by I2 receptor agonists was mediated by serotonergic and noradrenergic mechanisms with 5-HT1A , 5-HT2A and α1 -adrenoceptor being particularly important. In contrast, the hypothermic and discriminative stimulus effects of I2 receptor agonists were mediated by distinct, independent mechanisms.
© 2018 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
References
-
- National Research Council (2011). Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. edn, 10.17226/12910. National Academy of Sciences: Washington DC.
-
- Bardin L (2011). The complex role of serotonin and 5‐HT receptors in chronic pain. Behav Pharmacol 22: 390–404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

