Delta Opioids: Neuroprotective Roles in Preclinical Studies
- PMID: 29451852
- PMCID: PMC5963634
- DOI: 10.1089/jop.2017.0039
Delta Opioids: Neuroprotective Roles in Preclinical Studies
Abstract
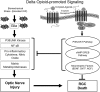
Since ancient times, opioids have been used clinically and abused recreationally. In the early stages (about 1,000 AD) of opium history, an Arab physician, Avicenna, administered opioids to control diarrhea and eye diseases. 1 Opioids have very strong pain relieving properties and they also regulate numerous cellular responses. Opioid receptors are expressed throughout the body, including the nervous system, heart, lungs, liver, gastrointestinal tract, and retina. 2-6 Delta opioid receptors (DORs) are a very attractive target from the perspective of both receptor function and their therapeutic potential. Due to a rapid progress in mouse mutagenesis and development of small molecules as DOR agonist, novel functions and roles of DORs have emerged in recent years. This review article focuses on the recent advances in the neuroprotective roles of DOR agonists in general and retina neuroprotection in particular. Rather than being exhaustive, this review highlights the selected studies of DOR function in neuroprotection. We also highlight our preclinical studies using rodent models to demonstrate the potentials of DOR agonists for retinal neuroprotection. Based on existing literature and our recently published data on the eye, DOR agonists possess therapeutic abilities that protect the retina and optic nerve injury against glaucoma and perhaps other retinopathies as well. This review also highlights the signaling events associated with DOR for neuroprotection in the eye. There is a need for translational research on DORs to recognize their potential for clinical application such as in glaucoma.
Keywords: glaucoma pharmacology; opioid receptors; retinal neuroprotection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial or proprietary interest in any product mentioned in this article.
Figures
References
-
- Norn S., Kruse P.R., and Kruse E. [History of opium poppy and morphine]. Dan. Medicinhist. Arbog. 33:171–184, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Husain S., Abdul Y., and Potter D.E. Non-analgesic effects of opioids: neuroprotection in the retina. Curr. Pharm. Des. 18:6101–6108, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Husain S., and Potter D.E. The opioidergic system: potential roles and therapeutic indications in the eye. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 24:117–140, 2008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

