Detection of Bartonella spp. in fleas by MALDI-TOF MS
- PMID: 29451890
- PMCID: PMC5833284
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006189
Detection of Bartonella spp. in fleas by MALDI-TOF MS
Abstract
Background: Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) has recently emerged in the field of entomology as a promising method for the identification of arthropods and the detection of associated pathogens.
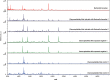
Methodology/principal findings: An experimental model of Ctenocephalides felis (cat fleas) infected with Bartonella quintana and Bartonella henselae was developed to evaluate the efficacy of MALDI-TOF MS in distinguishing infected from uninfected fleas, and its ability to distinguish fleas infected with Bartonella quintana from fleas infected with Bartonella henselae. For B. quintana, two groups of fleas received three successive blood meals, infected or not. A total of 140 fleas (100 exposed fleas and 40 control fleas) were engorged on human blood, infected or uninfected with B. quintana. Regarding the second pathogen, two groups of fleas (200 exposed fleas and 40 control fleas) were fed in the same manner with human blood, infected or not with Bartonella henselae. Fleas were dissected longitudinally; one-half was used for assessment of B. quintana and B. henselae infectious status by real-time PCR, and the second half was subjected to MALDI-TOF MS analysis. Comparison of MS spectra from infected fleas and uninfected fleas revealed distinct MS profiles. Blind queries against our MALDI-TOF MS arthropod database, upgraded with reference spectra from B. quintana and B. henselae infected fleas but also non-infected fleas, provided the correct classification for 100% of the different categories of specimens tested on the first model of flea infection with Bartonella quintana. As for Bartonella henselae, 81% of exposed qPCR-positive fleas, 96% of exposed qPCR-negative fleas and 100% of control fleas were correctly identified on the second model of flea infection. MALDI-TOF MS successfully differentiated Bartonella spp.-infected and uninfected fleas and was also able to correctly differentiate fleas infected with Bartonella quintana and fleas infected with Bartonella henselae. MALDI-TOF MS correctly identified flea species as well as their infectious status, consistent with the results of real-time PCR.
Conclusions/significance: MALDI-TOF is a promising tool for identification of the infection status of fleas infected with Bartonella spp., which allows new possibilities for fast and accurate diagnosis in medical entomology and vector surveillance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Bitam I, Dittmar K, Parola P, Whiting MF, Raoult D. Fleas and flea-borne diseases. Int J Infect Dis. 2010;14: e667–e676. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2009.11.011 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Leulmi H, Socolovschi C, Laudisoit A, Houemenou G, Davoust B, Bitam I, et al. Detection of Rickettsia felis, Rickettsia typhi, Bartonella Species and Yersinia pestis in Fleas (Siphonaptera) from Africa. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014;8: e3152 doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003152 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kernif T, Leulmi H, Socolovschi C, Berenger J-M, Lepidi H, Bitam I, et al. Acquisition and excretion of Bartonella quintana by the cat flea, Ctenocephalides felis felis. Mol Ecol. 2014;23: 1204–1212. doi: 10.1111/mec.12663 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Coulaud P-J, Lepolard C, Bechah Y, Berenger J-M, Raoult D, Ghigo E. Hemocytes from Pediculus humanus humanus are hosts for human bacterial pathogens. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014;4: 183 doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00183 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

