Clinical and genetic study of 20 patients from China with Cornelia de Lange syndrome
- PMID: 29452578
- PMCID: PMC5815176
- DOI: 10.1186/s12887-018-1004-3
Clinical and genetic study of 20 patients from China with Cornelia de Lange syndrome
Abstract
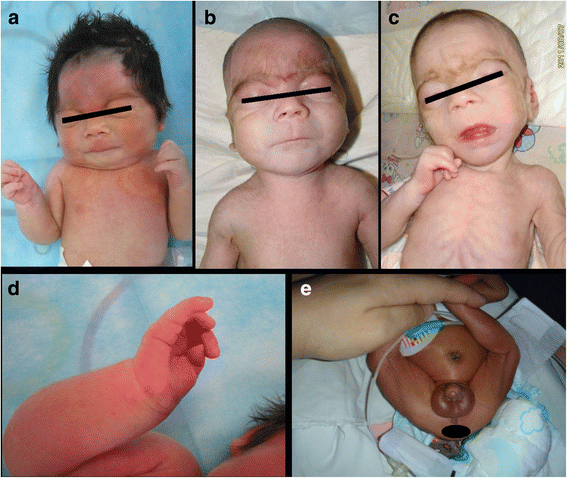
Background: Cornelia de Lange syndrome (CdLS) is a rare congenital syndrome with no racial difference. The objective of this study is to report the clinical characteristics and genetic study of 20 CdLS cases from China.
Methods: This is an observational study. Suspected patients were referred for further confirmation, clinical treatment, and genetic testing under voluntary condition. Demographic data and family history, data of clinical manifestations including facial dysmorphism and developmental delay of each patient were collected. Chromosomal analysis and NIPBL/SMC1A/SMC3 gene mutational analysis were carried out by PCR, reverse transcription PCR direct sequencing in the probands, and SNP array to detect the genome-wide copy number variations.
Results: Twenty CdLS cases from China were included in this study. Facial dysmorphisms, feeding difficulties, and developmental delay were the major clinical manifestations. Seven patients underwent gene mutation tests. Both the SMC1A and SMC3 gene mutation tests were negative in all. A heterozygous mutation in exon 20 of the NIPBL gene in proband 2, and a heterozygous mutation in intron 38 of the NIPBL gene in proband 3 were found in 1 patient, and RT-PCR revealed a splicing mutation in exon 38, generating both normal transcript and an aberrant alternatively spliced transcript with exon 38 deletion.
Conclusions: Clinical manifestations of CdLS patients from China are similar to those in the other countries. Heterozygous mutations of NIPBL gene were found.
Keywords: Child; China; Clinical; Cornelia de Lange syndrome; Genetic; Newborn.
Conflict of interest statement
Author’s information
Dr. Mingyan Hei, Pediatrician, M.D., Ph.D., ex-head of NICU of the Third Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, China. Now working as the vice-head of Neonatal Center of Beijing Children’s Hospital of Capital Medical University, Beijing, China. Dr. Xiangyu Gao, Pediatrician, M.D., vice director of Department of Pediatrics of Xuzhou Affiliated Hospital of East South University, Xuzhou, Jiangsu, China. Dr. Lingqian Wu, Obstetrician, M.D., Ph.D., chairman of Hunan Provincial Medical Genetic Committee, executive head of National Key Lab of Medical Genetics of Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, China.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was conducted in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration or comparable standards, and approved by the Ethics Committee Review Board of Central South University (No. 2011-S096). As common administrative policies, each hospital authorizes the registered staff to access patients’ data during their serves periods. Informed written consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
We got written consents from parents of the three CdLS neonates to allow us to publish the photos for research purpose (The scanned images of these consents are available for review if required).
Competing interests
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
De novo heterozygous mutations in SMC3 cause a range of Cornelia de Lange syndrome-overlapping phenotypes.Hum Mutat. 2015 Apr;36(4):454-62. doi: 10.1002/humu.22761. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Hum Mutat. 2015. PMID: 25655089
-
Mutation spectrum and genotype-phenotype correlation in Cornelia de Lange syndrome.Hum Mutat. 2013 Dec;34(12):1589-96. doi: 10.1002/humu.22430. Epub 2013 Sep 16. Hum Mutat. 2013. PMID: 24038889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intragenic and large NIPBL rearrangements revealed by MLPA in Cornelia de Lange patients.Eur J Hum Genet. 2012 Jul;20(7):734-41. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2012.7. Epub 2012 Feb 22. Eur J Hum Genet. 2012. PMID: 22353942 Free PMC article.
-
Global transcriptional disturbances underlie Cornelia de Lange syndrome and related phenotypes.J Clin Invest. 2015 Feb;125(2):636-51. doi: 10.1172/JCI77435. Epub 2015 Jan 9. J Clin Invest. 2015. PMID: 25574841 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cornelia de Lange syndrome.Clin Genet. 2015 Jul;88(1):1-12. doi: 10.1111/cge.12499. Epub 2014 Oct 28. Clin Genet. 2015. PMID: 25209348 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of clinical and genetic characteristics in 10 Chinese individuals with Cornelia de Lange syndrome and literature review.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020 Oct;8(10):e1471. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1471. Epub 2020 Aug 27. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020. PMID: 32856424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Broader Perspective on the Prenatal Diagnosis of Cornelia de Lange Syndrome: Review of the Literature and Case Presentation.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Jan 19;11(1):142. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11010142. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33478103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive genetic analysis of 57 families with clinically suspected Cornelia de Lange syndrome.J Hum Genet. 2019 Oct;64(10):967-978. doi: 10.1038/s10038-019-0643-z. Epub 2019 Jul 23. J Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 31337854
-
Whole Genome Sequencing of "Mutation-Negative" Individuals With Cornelia de Lange Syndrome.Hum Mutat. 2025 Jan 30;2025:4711663. doi: 10.1155/humu/4711663. eCollection 2025. Hum Mutat. 2025. PMID: 40677927 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu J, Baynam G. Cornelia de Lange syndrome. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;685:111–123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

