Ubiquitin-Mediated Regulation of RIPK1 Kinase Activity Independent of IKK and MK2
- PMID: 29452637
- PMCID: PMC5823975
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.01.027
Ubiquitin-Mediated Regulation of RIPK1 Kinase Activity Independent of IKK and MK2
Abstract
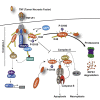
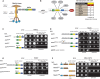
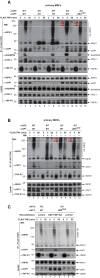
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) can drive inflammation, cell survival, and death. While ubiquitylation-, phosphorylation-, and nuclear factor κB (NF-κB)-dependent checkpoints suppress the cytotoxic potential of TNF, it remains unclear whether ubiquitylation can directly repress TNF-induced death. Here, we show that ubiquitylation regulates RIPK1's cytotoxic potential not only via activation of downstream kinases and NF-kB transcriptional responses, but also by directly repressing RIPK1 kinase activity via ubiquitin-dependent inactivation. We find that the ubiquitin-associated (UBA) domain of cellular inhibitor of apoptosis (cIAP)1 is required for optimal ubiquitin-lysine occupancy and K48 ubiquitylation of RIPK1. Independently of IKK and MK2, cIAP1-mediated and UBA-assisted ubiquitylation suppresses RIPK1 kinase auto-activation and, in addition, marks it for proteasomal degradation. In the absence of a functional UBA domain of cIAP1, more active RIPK1 kinase accumulates in response to TNF, causing RIPK1 kinase-mediated cell death and systemic inflammatory response syndrome. These results reveal a direct role for cIAP-mediated ubiquitylation in controlling RIPK1 kinase activity and preventing TNF-mediated cytotoxicity.
Keywords: RIPK1; TNF; apoptosis; cIAPs; caspase-8; cell death; inflammation; necroptosis; ubiquitin.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Annibaldi A., Meier P. Checkpoints in TNF-induced cell death: implications in inflammation and cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 2018;24:49–65. - PubMed
-
- Bertrand M.J., Milutinovic S., Dickson K.M., Ho W.C., Boudreault A., Durkin J., Gillard J.W., Jaquith J.B., Morris S.J., Barker P.A. cIAP1 and cIAP2 facilitate cancer cell survival by functioning as E3 ligases that promote RIP1 ubiquitination. Mol. Cell. 2008;30:689–700. - PubMed
-
- Bettermann K., Vucur M., Haybaeck J., Koppe C., Janssen J., Heymann F., Weber A., Weiskirchen R., Liedtke C., Gassler N. TAK1 suppresses a NEMO-dependent but NF-kappaB-independent pathway to liver cancer. Cancer Cell. 2010;17:481–496. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

