β-catenin-independent regulation of Wnt target genes by RoR2 and ATF2/ATF4 in colon cancer cells
- PMID: 29453334
- PMCID: PMC5816634
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-20641-5
β-catenin-independent regulation of Wnt target genes by RoR2 and ATF2/ATF4 in colon cancer cells
Abstract
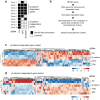
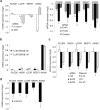
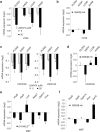
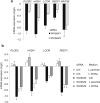
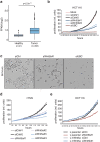
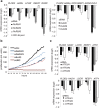
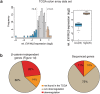
Wnt signaling is an evolutionarily conserved signaling route required for development and homeostasis. While canonical, β-catenin-dependent Wnt signaling is well studied and has been linked to many forms of cancer, much less is known about the role of non-canonical, β-catenin-independent Wnt signaling. Here, we aimed at identifying a β-catenin-independent Wnt target gene signature in order to understand the functional significance of non-canonical signaling in colon cancer cells. Gene expression profiling was performed after silencing of key components of Wnt signaling pathway and an iterative signature algorithm was applied to predict pathway-dependent gene signatures. Independent experiments confirmed several target genes, including PLOD2, HADH, LCOR and REEP1 as non-canonical target genes in various colon cancer cells. Moreover, non-canonical Wnt target genes are regulated via RoR2, Dvl2, ATF2 and ATF4. Furthermore, we show that the ligands Wnt5a/b are upstream regulators of the non-canonical signature and moreover regulate proliferation of cancer cells in a β-catenin-independent manner. Our experiments indicate that colon cancer cells are dependent on both β-catenin-dependent and -independent Wnt signaling routes for growth and proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Roelink H, Wagenaar E, Nusse R. Amplification and proviral activation of several Wnt genes during progression and clonal variation of mouse mammary tumors. Oncogene. 1992;7:487–492. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

