Alterations in interhemispheric gamma-band connectivity are related to the emergence of auditory verbal hallucinations in healthy subjects during NMDA-receptor blockade
- PMID: 29453445
- PMCID: PMC5983549
- DOI: 10.1038/s41386-018-0014-z
Alterations in interhemispheric gamma-band connectivity are related to the emergence of auditory verbal hallucinations in healthy subjects during NMDA-receptor blockade
Abstract
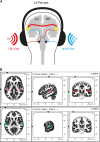
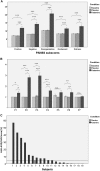
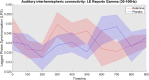
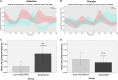
Auditory verbal hallucinations (AVH) are a common positive symptom of schizophrenia. Excitatory-to-inhibitory (E/I) imbalance related to disturbed N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) functioning has been suggested as a possible mechanism underlying altered connectivity and AVH in schizophrenia. The current study examined the effects of ketamine, a NMDAR antagonist, on glutamate-related mechanisms underlying interhemispheric gamma-band connectivity, conscious auditory perception during dichotic listening (DL), and the emergence of auditory verbal distortions and hallucinations (AVD/AVH) in healthy volunteers. In a single-blind, pseudo-randomized, placebo-controlled crossover design, nineteen male, right-handed volunteers were measured using 64 channel electroencephalography (EEG). Psychopathology was assessed with the PANSS interview and the 5D-ASC questionnaire, including a subscale to detect auditory alterations with regard to AVD/AVH (AUA-AVD/AVH). Interhemispheric connectivity analysis was performed using eLORETA source estimation and lagged phase synchronization (LPS) in the gamma-band range (30-100 Hz). Ketamine induced positive symptoms such as hallucinations in a subgroup of healthy subjects. In addition, interhemispheric gamma-band connectivity was found to be altered under ketamine compared to placebo, and subjects with AUA-AVD/AVH under ketamine showed significantly higher interhemispheric gamma-band connectivity than subjects without AUA-AVD/AVH. These findings demonstrate a relationship between NMDAR functioning, interhemispheric connectivity in the gamma-band frequency range between bilateral auditory cortices and the emergence of AVD/AVH in healthy subjects. The result is in accordance with the interhemispheric miscommunication hypothesis of AVH and argues for a possible role of glutamate in AVH in schizophrenia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

