Systematic and stochastic influences on the performance of the MinION nanopore sequencer across a range of nucleotide bias
- PMID: 29453452
- PMCID: PMC5816649
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-21484-w
Systematic and stochastic influences on the performance of the MinION nanopore sequencer across a range of nucleotide bias
Abstract
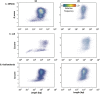
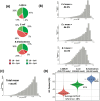
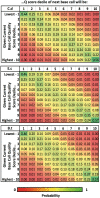
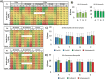
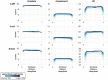
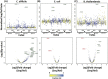
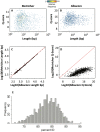
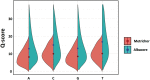
Emerging sequencing technologies are allowing us to characterize environmental, clinical and laboratory samples with increasing speed and detail, including real-time analysis and interpretation of data. One example of this is being able to rapidly and accurately detect a wide range of pathogenic organisms, both in the clinic and the field. Genomes can have radically different GC content however, such that accurate sequence analysis can be challenging depending upon the technology used. Here, we have characterized the performance of the Oxford MinION nanopore sequencer for detection and evaluation of organisms with a range of genomic nucleotide bias. We have diagnosed the quality of base-calling across individual reads and discovered that the position within the read affects base-calling and quality scores. Finally, we have evaluated the performance of the current state-of-the-art neural network-based MinION basecaller, characterizing its behavior with respect to systemic errors as well as context- and sequence-specific errors. Overall, we present a detailed characterization the capabilities of the MinION in terms of generating high-accuracy sequence data from genomes with a wide range of nucleotide content. This study provides a framework for designing the appropriate experiments that are the likely to lead to accurate and rapid field-forward diagnostics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

