Regulation of Blood-Testis Barrier (BTB) Dynamics, Role of Actin-, and Microtubule-Based Cytoskeletons
- PMID: 29453575
- PMCID: PMC5963684
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7698-0_16
Regulation of Blood-Testis Barrier (BTB) Dynamics, Role of Actin-, and Microtubule-Based Cytoskeletons
Abstract
The blood-testis barrier (BTB) is an important ultrastructure in the testis that supports meiosis and postmeiotic spermatid development since a delay in the establishment of a functional Sertoli cell barrier during postnatal development in rats or mice by 17-20 day postpartum (dpp) would lead to a delay of the first wave of meiosis. Furthermore, irreversible disruption of the BTB by toxicants also induces infertility in rodents. Herein, we summarize recent findings that BTB dynamics (i.e., disassembly, reassembly, and stabilization) are supported by the concerted efforts of the actin- and microtubule (MT)-based cytoskeletons. We focus on the role of two actin nucleation protein complexes, namely, the Arp2/3 (actin-related protein 2/3) complex and formin 1 (or the formin 1/spire 1 complex) known to induce actin nucleation, respectively, by conferring plasticity to actin cytoskeleton. We also focus on the MT plus (+)-end tracking protein (+TIP) EB1 (end-binding protein 1) which is known to confer MT stabilization. Furthermore, we discuss in particular how the interactions of these proteins modulate BTB dynamics during spermatogenesis. These findings also yield a novel hypothetical concept regarding the molecular mechanism that modulates BTB function.
Keywords: Blood-testis barrier; Desmosome; Ectoplasmic specialization; Gap junction; Seminiferous epithelial cycle; Sertoli cell; Spermatogenesis; Testis; Tight junction.
Figures

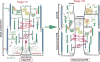
Similar articles
-
Transport of germ cells across the seminiferous epithelium during spermatogenesis-the involvement of both actin- and microtubule-based cytoskeletons.Tissue Barriers. 2016 Nov 28;4(4):e1265042. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2016.1265042. eCollection 2016. Tissue Barriers. 2016. PMID: 28123928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Basement Membrane Laminin α2 Regulation of BTB Dynamics via Its Effects on F-Actin and Microtubule Cytoskeletons Is Mediated Through mTORC1 Signaling.Endocrinology. 2017 Apr 1;158(4):963-978. doi: 10.1210/en.2016-1630. Endocrinology. 2017. PMID: 28323988 Free PMC article.
-
KIF15 supports spermatogenesis via its effects on Sertoli cell microtubule, actin, vimentin, and septin cytoskeletons.Endocrinology. 2021 Apr 1;162(4):bqab010. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqab010. Endocrinology. 2021. PMID: 33453102 Free PMC article.
-
CAMSAP2 Is a Microtubule Minus-End Targeting Protein That Regulates BTB Dynamics Through Cytoskeletal Organization.Endocrinology. 2019 Jun 1;160(6):1448-1467. doi: 10.1210/en.2018-01097. Endocrinology. 2019. PMID: 30994903 Free PMC article.
-
NC1-peptide derived from collagen α3 (IV) chain is a blood-tissue barrier regulator: lesson from the testis.Asian J Androl. 2021 Mar-Apr;23(2):123-128. doi: 10.4103/aja.aja_44_20. Asian J Androl. 2021. PMID: 32896837 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Physiological role of actin regulation in male fertility: Insight into actin capping proteins in spermatogenic cells.Reprod Med Biol. 2020 Jan 22;19(2):120-127. doi: 10.1002/rmb2.12316. eCollection 2020 Apr. Reprod Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32273816 Free PMC article.
-
Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Infection Compromises the Blood-Testis Barrier by Disturbing mTORC1-mTORC2 Balance.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 19;12:582858. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.582858. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33679734 Free PMC article.
-
ALKBH5 in mouse testicular Sertoli cells regulates Cdh2 mRNA translation to maintain blood-testis barrier integrity.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022 Nov 22;27(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s11658-022-00404-x. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022. PMID: 36418936 Free PMC article.
-
FYN regulates cell adhesion at the blood-testis barrier and the apical ectoplasmic specialization via its effect on Arp3 in the mouse testis.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 9;13:915274. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.915274. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36016954 Free PMC article.
-
Busulfan damages spermatogenic function by inducing orchitis.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 22;20(7):e0322721. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0322721. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40694571 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pelletier RM. The blood-testis barrier: the junctional permeability, the proteins and the lipids. Prog Histochem Cytochem. 2011;46:49–127. - PubMed
-
- Stanton PG. Regulation of the blood-testis barrier. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016;59:166–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.06.018. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mruk DD, Cheng CY. The mammalian blood-testis barrier: its biology and regulation. Endocr Rev. 2015;36(5):564–591. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2014-1101. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- O’Donnell L, O’Bryan MK. Microtubules and spermatogenesis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014;30:45–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.01.003. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

