Sleep apnea and type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 29453905
- PMCID: PMC6123041
- DOI: 10.1111/jdi.12823
Sleep apnea and type 2 diabetes
Abstract
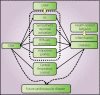
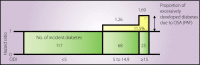
The aim of the present review was to clarify the association between obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and type 2 diabetes, and discuss the therapeutic role of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) in type 2 diabetes. OSA patients are more likely than non-OSA populations to develop type 2 diabetes, while more than half of type 2 diabetes patients suffer from OSA. Similar to Western countries, in the East Asian population, the association between these two disorders has also been reported. CPAP is the primary treatment for OSA, but the effect of CPAP on comorbid diabetes has not been established. CPAP improved glucose metabolism determined by the oral glucose tolerance test in OSA patients, and several studies have shown that CPAP improves insulin resistance, particularly in obese populations undergoing long-term CPAP. Diabetes is associated with other sleep-related manifestations as well, such as snoring and excessive daytime sleepiness. Snoring is associated with the development of diabetes, and excessive daytime sleepiness appears to modify insulin resistance. Well-designed studies are required to clarify the therapeutic effect of CPAP on diabetes. As both diabetes and OSA lead to cardiovascular disease, clinicians and healthcare professionals should be aware of the association between diabetes and OSA, and should take CPAP and health-related behaviors into consideration when treating patients with diabetes and/or OSA.
Keywords: Continuous positive airway pressure; Diabetes; Sleep apnea.
© 2018 The Authors. Journal of Diabetes Investigation published by Asian Association for the Study of Diabetes (AASD) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Xu J, Long YS, Gozal D, et al Beta‐cell death and proliferation after intermittent hypoxia: role of oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 2009; 46: 783–790. - PubMed
-
- Anothaisintawee T, Reutrakul S, Van Cauter E, et al Sleep disturbances compared to traditional risk factors for diabetes development: systematic review and meta‐analysis. Sleep Med Rev 2016; 30: 11–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

