High and low doses of cocaine intake are differentially regulated by dopamine D2 receptors in the ventral tegmental area and the nucleus accumbens
- PMID: 29454035
- PMCID: PMC5972382
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2018.02.026
High and low doses of cocaine intake are differentially regulated by dopamine D2 receptors in the ventral tegmental area and the nucleus accumbens
Abstract
Dopamine D2 receptors (D2Rs) in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and the nucleus accumbens (NAc) are associated with vulnerability to addiction; however, whether D2Rs in these two brain regions play differential roles in regulation of drug intake is unknown. Here, we compared the effect of decreased mRNA level of Drd2 in each region on cocaine self-administration in a dose-response function. Drd2 mRNA levels in rat VTA or NAc were knocked down by bilateral microinjection of lentivirus coding shRNAs against rat Drd2 or scrambled shRNA. Drd2 knockdown was persistent and stable between 20 and 90 days after lentiviral infection. Animals were trained to self-administer cocaine 20 days after Drd2 shRNA treatment. Compared to scrambled shRNA treated rats, Drd2 knockdown in the VTA increased cocaine self-administration at all tested doses (0.02-0.56 mg/kg/infusion) producing an upward shift (both the ascending and descending limb) in the dose-response curve of cocaine self-administration. In contrast, intra-NAc knockdown increased cocaine self-administration only on the ascending limb of the dose-response curve (0.02-0.07 mg/kg/infusion). These data suggest that D2Rs in the VTA, not in the NAc, regulate high-dose cocaine intake. The present study not only demonstrates that low levels of D2Rs in either region increase low doses of cocaine intake, but also reveals for the first time their dissociable roles in limiting high doses of cocaine self-administration.
Keywords: Cocaine self-administration; Dopamine D2 autoreceptors; Drd2 knockdown; Nucleus accumbens; Ventral tegmental area.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
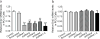
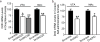
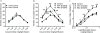
References
-
- Lee B, London ED, Poldrack RA, Farahi J, Nacca A, Monterosso JR, Mumford JA, Bokarius AV, Dahlbom M, Mukherjee J, Bilder RM, Brody AL, Mandelkern MA. Striatal dopamine d2/d3 receptor availability is reduced in methamphetamine dependence and is linked to impulsivity. J Neurosci. 2009;29:14734–14740. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Thanos PP, Logan J, Gatley SJ, Gifford A, Ding YS, Wong C, Pappas N. Brain DA D2 receptors predict reinforcing effects of stimulants in humans: replication study. Synapse. 2002;46:79–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

