Nutraceuticals as therapeutic agents for atherosclerosis
- PMID: 29454074
- PMCID: PMC5906642
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.02.006
Nutraceuticals as therapeutic agents for atherosclerosis
Abstract
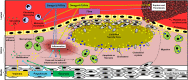
Atherosclerosis, a chronic inflammatory disorder of medium and large arteries and an underlying cause of cardiovascular disease (CVD), is responsible for a third of all global deaths. Current treatments for CVD, such as optimized statin therapy, are associated with considerable residual risk and several side effects in some patients. The outcome of research on the identification of alternative pharmaceutical agents for the treatment of CVD has been relatively disappointing with many promising leads failing at the clinical level. Nutraceuticals, products from food sources with health benefits beyond their nutritional value, represent promising agents in the prevention of CVD or as an add-on therapy with current treatments. This review will highlight the potential of several nutraceuticals, including polyunsaturated fatty acids, flavonoids and other polyphenols, as anti-CVD therapies based on clinical and pre-clinical mechanism-based studies.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Cardiovascular disease; Nutraceuticals; Polyphenols; Polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Buckley M.L., Ramji D.P. The influence of dysfunctional signaling and lipid homeostasis in mediating the inflammatory responses during atherosclerosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2015;1852:1498–1510. - PubMed
-
- McLaren J.E., Michael D.R., Ashlin T.G., Ramji D.P. Cytokines, macrophage lipid metabolism and foam cells: implications for cardiovascluar disease therapy. Prog. Lipid Res. 2011;50:331–347. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

