P300 Acetyltransferase Mediates Stiffness-Induced Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells Into Tumor-Promoting Myofibroblasts
- PMID: 29454793
- PMCID: PMC6039101
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.02.015
P300 Acetyltransferase Mediates Stiffness-Induced Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells Into Tumor-Promoting Myofibroblasts
Abstract
Background & aims: Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) contribute to desmoplasia and stiffness of liver metastases by differentiating into matrix-producing myofibroblasts. We investigated whether stiffness due to the presence of tumors increases activation of HSCs into myofibroblasts and their tumor-promoting effects, as well as the role of E1A binding protein p300, a histone acetyltransferase that regulates transcription, in these processes.
Methods: HSCs were isolated from liver tissues of patients, mice in which the p300 gene was flanked by 2 loxP sites (p300F/F mice), and p300+/+ mice (controls). The HSCs were placed on polyacrylamide gels with precisely defined stiffness, and their activation (differentiation into myofibroblasts) was assessed by immunofluorescence and immunoblot analyses for alpha-smooth muscle actin. In HSCs from mice, the p300 gene was disrupted by cre recombinase. In human HSCs, levels of p300 were knocked down with small hairpin RNAs or a mutant form of p300 that is not phosphorylated by AKT (p300S1834A) was overexpressed. Human HSCs were also cultured with inhibitors of p300 (C646), PI3K signaling to AKT (LY294002), or RHOA (C3 transferase) and effects on stiffness-induced activation were measured. RNA sequencing and chromatin immunoprecipitation-quantitative polymerase chain reaction were used to identify HSC genes that changed expression levels in response to stiffness. We measured effects of HSC-conditioned media on proliferation of HT29 colon cancer cells and growth of tumors following subcutaneous injection of these cells into mice. MC38 colon cancer cells were injected into portal veins of p300F/Fcre and control mice, and liver metastases were measured. p300F/Fcre and control mice were given intraperitoneal injections of CCl4 to induce liver fibrosis. Liver tissues were collected and analyzed by immunofluorescence, immunoblot, and histology.
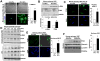
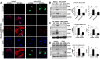
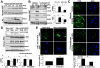
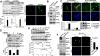
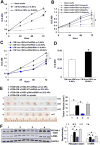
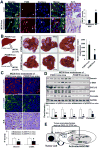
Results: Substrate stiffness was sufficient to activate HSCs, leading to nuclear accumulation of p300. Disrupting p300 level or activity blocked stiffness-induced activation of HSCs. In HSCs, substrate stiffness activated AKT signaling via RHOA to induce phosphorylation of p300 at serine 1834; this caused p300 to translocate to the nucleus, where it up-regulated transcription of genes that increase activation of HSCs and metastasis, including CXCL12. MC38 cells, injected into portal veins, formed fewer metastases in livers of p300F/Fcre mice than control mice. Expression of p300 was increased in livers of mice following injection of CCl4; HSC activation and collagen deposition were reduced in livers of p300F/Fcre mice compared with control mice.
Conclusions: In studies of mice, we found liver stiffness to activate HSC differentiation into myofibroblasts, which required nuclear accumulation of p300. p300 increases HSC expression of genes that promote metastasis.
Keywords: Chromatin Remodeling; Epigenetic Modification; Mechanotransduction; Tumor Progression.
Copyright © 2018 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
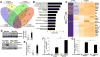
Comment in
-
P300, A New Player in Mechanosensitivity and Activation of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts.Gastroenterology. 2018 Jun;154(8):2025-2026. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.05.002. Epub 2018 May 5. Gastroenterology. 2018. PMID: 29733834 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

