Defining G protein-coupled receptor peptide ligand expressomes and signalomes in human and mouse islets
- PMID: 29455414
- PMCID: PMC6061145
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-018-2778-z
Defining G protein-coupled receptor peptide ligand expressomes and signalomes in human and mouse islets
Abstract
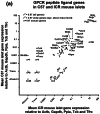
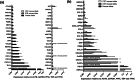
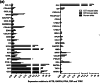
Introduction: Islets synthesise and secrete numerous peptides, some of which are known to be important regulators of islet function and glucose homeostasis. In this study, we quantified mRNAs encoding all peptide ligands of islet G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) in isolated human and mouse islets and carried out in vitro islet hormone secretion studies to provide functional confirmation for the species-specific role of peptide YY (PYY) in mouse islets.
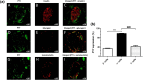
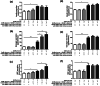
Materials and methods: GPCR peptide ligand mRNAs in human and mouse islets were quantified by quantitative real-time PCR relative to the reference genes ACTB, GAPDH, PPIA, TBP and TFRC. The pathways connecting GPCR peptide ligands with their receptors were identified by manual searches in the PubMed, IUPHAR and Ingenuity databases. Distribution of PYY protein in mouse and human islets was determined by immunohistochemistry. Insulin, glucagon and somatostatin secretion from islets was measured by radioimmunoassay.
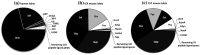
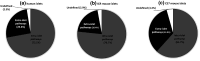
Results: We have quantified GPCR peptide ligand mRNA expression in human and mouse islets and created specific signalomes mapping the pathways by which islet peptide ligands regulate human and mouse GPCR signalling. We also identified species-specific islet expression of several GPCR ligands. In particular, PYY mRNA levels were ~ 40,000-fold higher in mouse than human islets, suggesting a more important role of locally secreted Pyy in mouse islets. This was confirmed by IHC and functional experiments measuring insulin, glucagon and somatostatin secretion.
Discussion: The detailed human and mouse islet GPCR peptide ligand atlases will allow accurate translation of mouse islet functional studies for the identification of GPCR/peptide signalling pathways relevant for human physiology, which may lead to novel treatment modalities of diabetes and metabolic disease.
Keywords: GPCRs; Islets of Langerhans; PYY; Peptide ligands; Type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Jones PM, Persaud SJ. Islet function and insulin secretion textbook of diabetes. 5. Chichester: Wiley; 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

