The effects of interleukin-33 on airways collagen deposition and matrix metalloproteinase expression in a murine surrogate of asthma
- PMID: 29455466
- PMCID: PMC6050212
- DOI: 10.1111/imm.12911
The effects of interleukin-33 on airways collagen deposition and matrix metalloproteinase expression in a murine surrogate of asthma
Abstract
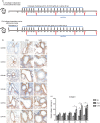
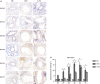
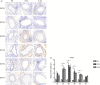
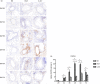
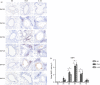
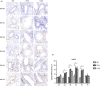
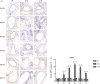
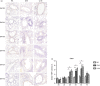
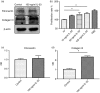
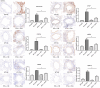
It has been suggested that interleukin-33 (IL-33) plays an important role in the pathogenesis of asthma through a variety of pathways, but its role in airways fibrosis in asthma has not been fully elucidated. In the present study we evaluated changes in the expression of extracellular matrix proteins (ECMs) as well as matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their inhibitors (TIMPs) in an IL-33-induced, antigen-independent murine surrogate of asthma as well as a conventional surrogate employing per-nasal challenge of mice previously sensitized to produce an IgE response to ovalbumin (OVA). In addition, in in vitro experiments we explored the direct effects of IL-33 on the proliferation and function of murine fibroblasts. Per-nasal administration of IL-33 alone was sufficient to induce airways deposition of ECMs, including collagens I, III, V and fibronectin, to a degree comparable with that observed in the OVA-sensitized and challenged mice. These changes were associated with a local imbalance between the expression of extracellular MMPs and TIMPs. Per-nasal challenge of mice with IL-33 also induced elevated airways expression of connective tissue growth factor and fibroblast growth factor receptor 4, two key facilitators of local fibrosis, again to a degree compatible with that observed in OVA-sensitized and challenged mice. Deletion of the ST2 gene, which encodes the IL-33 receptor, abrogated these fibrotic changes in the airways in the OVA surrogate. In vitro, IL-33 significantly increased the proliferation and expression of collagen III by murine lung fibroblasts. These data suggest that direct exposure of murine airways to IL-33 is able to induce local fibrotic changes, at least partially through effects of signalling through the IL-33/ST2 axis on fibroblast function and local expression of MMPs and their inhibitors, and other fibrosis-related proteins.
Keywords: asthma; fibrosis; interleukin-33; pathogenesis; remodelling.
© 2018 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characteristics of IL-25 and allergen-induced airway fibrosis in a murine model of asthma.Respirology. 2015 Jul;20(5):730-8. doi: 10.1111/resp.12546. Epub 2015 Apr 30. Respirology. 2015. PMID: 25929748
-
Nasal administration of interleukin-33 induces airways angiogenesis and expression of multiple angiogenic factors in a murine asthma surrogate.Immunology. 2016 May;148(1):83-91. doi: 10.1111/imm.12589. Epub 2016 Mar 8. Immunology. 2016. PMID: 27035894 Free PMC article.
-
Combined blockade of IL-25, IL-33 and TSLP mediates amplified inhibition of airway inflammation and remodelling in a murine model of asthma.Respirology. 2020 Jun;25(6):603-612. doi: 10.1111/resp.13711. Epub 2019 Oct 14. Respirology. 2020. PMID: 31610614
-
Expression and effects of IL-33 and ST2 in allergic bronchial asthma: IL-33 induces eotaxin production in lung fibroblasts.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2011;155 Suppl 1:12-20. doi: 10.1159/000327259. Epub 2011 Jun 1. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21646790
-
Cigarette smoke aggravates asthma via altering airways inflammation phenotypes and remodelling.Clin Respir J. 2023 Dec;17(12):1316-1327. doi: 10.1111/crj.13718. Epub 2023 Nov 14. Clin Respir J. 2023. PMID: 37963721 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
IL-33/ST2 Axis in Organ Fibrosis.Front Immunol. 2018 Oct 24;9:2432. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02432. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30405626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-33 Initiates Vascular Remodelling in Hypoxic Pulmonary Hypertension by up-Regulating HIF-1α and VEGF Expression in Vascular Endothelial Cells.EBioMedicine. 2018 Jul;33:196-210. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.06.003. Epub 2018 Jun 18. EBioMedicine. 2018. PMID: 29921553 Free PMC article.
-
Contributions of IL-33 in Non-hematopoietic Lung Cells to Obstructive Lung Disease.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 13;11:1798. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01798. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32903501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined Extracts of Epimedii Folium and Ligustri Lucidi Fructus with Budesonide Attenuate Airway Remodeling in the Asthmatic Rats by Regulating Apoptosis and Autophagy.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Aug 5;2020:2319409. doi: 10.1155/2020/2319409. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32831860 Free PMC article.
-
Piperlongumine reduces ovalbumin‑induced asthma and airway inflammation by regulating nuclear factor‑κB activation.Int J Mol Med. 2019 Nov;44(5):1855-1865. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4322. Epub 2019 Aug 21. Int J Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31485644 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Becker AB, Abrams EM. Asthma guidelines: the Global Initiative for Asthma in relation to national guidelines. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 2017; 17:99–103. - PubMed
-
- Weiler JM, Anderson SD, Randolph C, Bonini S, Craig TJ, Pearlman DS et al Pathogenesis, prevalence, diagnosis, and management of exercise‐induced bronchoconstriction: a practice parameter. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2010; 105:S1–47. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

