Role of Bruton's tyrosine kinase in B cells and malignancies
- PMID: 29455639
- PMCID: PMC5817726
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-018-0779-z
Role of Bruton's tyrosine kinase in B cells and malignancies
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Role of Bruton's tyrosine kinase in B cells and malignancies.Mol Cancer. 2019 Apr 3;18(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1009-z. Mol Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30943993 Free PMC article.
Abstract
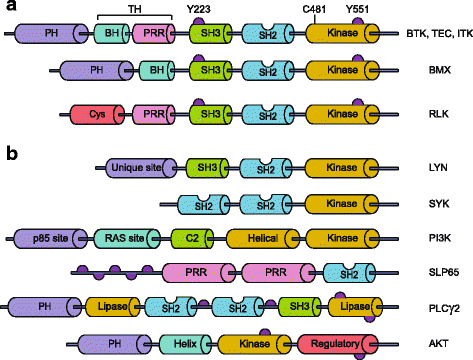
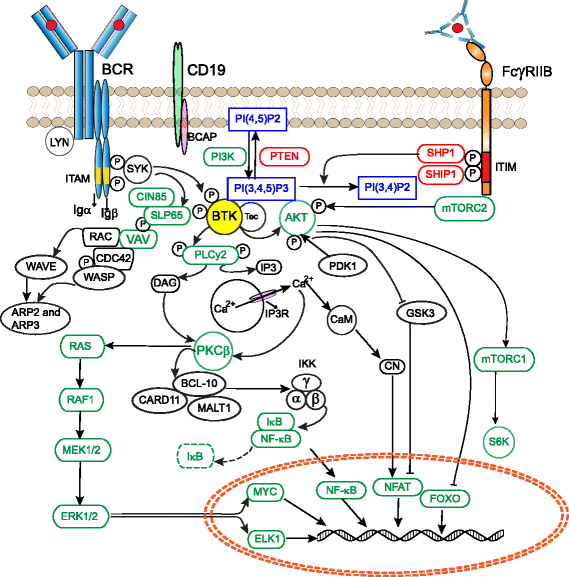
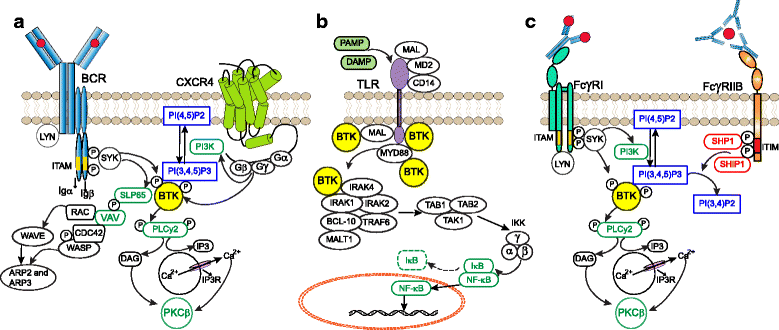
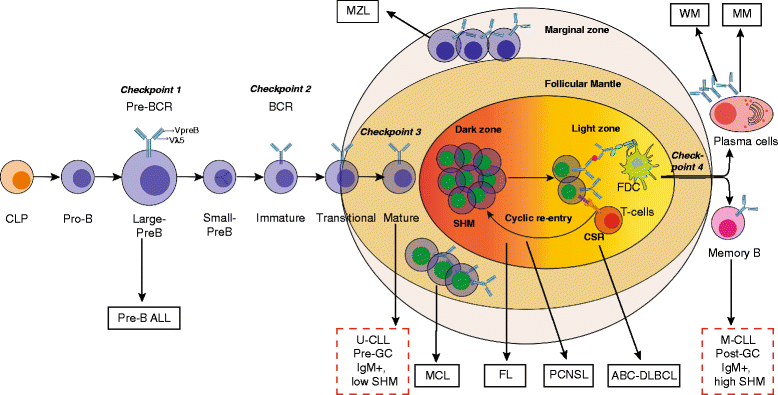
Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) is a non-receptor kinase that plays a crucial role in oncogenic signaling that is critical for proliferation and survival of leukemic cells in many B cell malignancies. BTK was initially shown to be defective in the primary immunodeficiency X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA) and is essential both for B cell development and function of mature B cells. Shortly after its discovery, BTK was placed in the signal transduction pathway downstream of the B cell antigen receptor (BCR). More recently, small-molecule inhibitors of this kinase have shown excellent anti-tumor activity, first in animal models and subsequently in clinical studies. In particular, the orally administered irreversible BTK inhibitor ibrutinib is associated with high response rates in patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and mantle-cell lymphoma (MCL), including patients with high-risk genetic lesions. Because ibrutinib is generally well tolerated and shows durable single-agent efficacy, it was rapidly approved for first-line treatment of patients with CLL in 2016. To date, evidence is accumulating for efficacy of ibrutinib in various other B cell malignancies. BTK inhibition has molecular effects beyond its classic role in BCR signaling. These involve B cell-intrinsic signaling pathways central to cellular survival, proliferation or retention in supportive lymphoid niches. Moreover, BTK functions in several myeloid cell populations representing important components of the tumor microenvironment. As a result, there is currently a considerable interest in BTK inhibition as an anti-cancer therapy, not only in B cell malignancies but also in solid tumors. Efficacy of BTK inhibition as a single agent therapy is strong, but resistance may develop, fueling the development of combination therapies that improve clinical responses. In this review, we discuss the role of BTK in B cell differentiation and B cell malignancies and highlight the importance of BTK inhibition in cancer therapy.
Keywords: B cell development; B cell receptor signaling; Bruton’s tyrosine kinase; Chemokine receptor; Chronic lymphocytic leukemia; Ibrutinib; Leukemia; Lymphoma; Tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

