Third generation EGFR TKIs: current data and future directions
- PMID: 29455654
- PMCID: PMC5817792
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-018-0778-0
Third generation EGFR TKIs: current data and future directions
Abstract
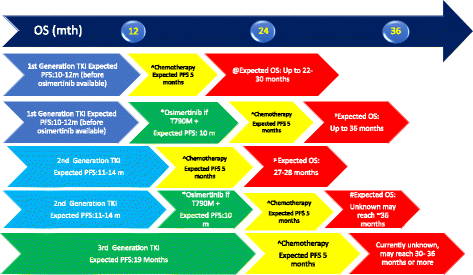
Acquired T790 M mutation is the commonest cause of resistance for advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutant patients who had progressed after first line EGFR TKI (tyrosine kinase inhibitor). Several third generation EGFR TKIs which are EGFR mutant selective and wild-type (WT) sparing were developed to treat these patients with T790 M acquired resistant mutation. Osimertinib is one of the third generation EGFR TKIs and is currently the most advanced in clinical development. Unfortunately, despite good initial response, patients who was treated with third generation EGFR TKI would develop acquired resistance and several mechanisms had been identified and the commonest being C797S mutation at exon 20. Several novel treatment options were being developed for patients who had progressed on third generation EGFR TKI but they are still in the early phase of development. Osimertinib under FLAURA study had been shown to have better progression-free survival over first generation EGFR TKI in the first line setting and likely will become the new standard of care.
Keywords: FLAURA; Osimertinib; Resistance mechanism; Sequencing; T790 M; Third generation EGFR TKI.
Conflict of interest statement
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, Negoro S, Okamoto I, Tsurutani J, Seto T, Satouchi M, Tada H, Hirashima T, et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. The Lancet Oncol. 2010;11(2):121–128. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70364-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, Feng J, Liu XQ, Wang C, Zhang S, Wang J, Zhou S, Ren S, et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. The Lancet Oncol. 2011;12(8):735–742. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70184-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, Vergnenegre A, Massuti B, Felip E, Palmero R, Garcia-Gomez R, Pallares C, Sanchez JM, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. The Lancet Oncol. 2012;13(3):239–246. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70393-X. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

