KRAS oncogene in non-small cell lung cancer: clinical perspectives on the treatment of an old target
- PMID: 29455666
- PMCID: PMC5817724
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-018-0789-x
KRAS oncogene in non-small cell lung cancer: clinical perspectives on the treatment of an old target
Abstract
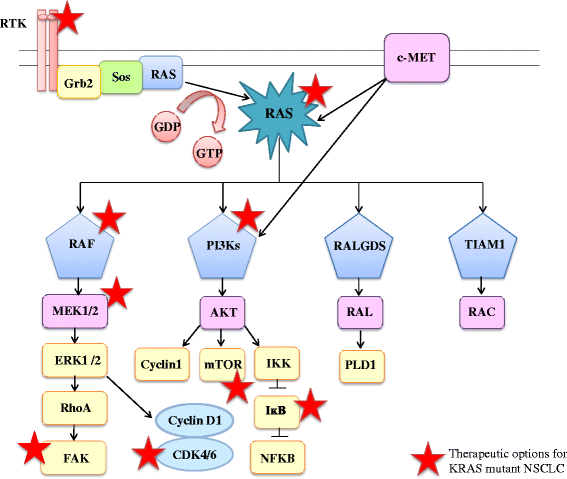
Lung neoplasms are the leading cause of death by cancer worldwide. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) constitutes more than 80% of all lung malignancies and the majority of patients present advanced disease at onset. However, in the last decade, multiple oncogenic driver alterations have been discovered and each of them represents a potential therapeutic target. Although KRAS mutations are the most frequently oncogene aberrations in lung adenocarcinoma patients, effective therapies targeting KRAS have yet to be developed. Moreover, the role of KRAS oncogene in NSCLC remains unclear and its predictive and prognostic impact remains controversial. The study of the underlying biology of KRAS in NSCLC patients could help to determine potential candidates to evaluate novel targeted agents and combinations that may allow a tailored treatment for these patients. The aim of this review is to update the current knowledge about KRAS-mutated lung adenocarcinoma, including a historical overview, the biology of the molecular pathways involved, the clinical relevance of KRAS mutations as a prognostic and predictive marker and the potential therapeutic approaches for a personalized treatment of KRAS-mutated NSCLC patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous