Management protocols for chronic heart failure in India
- PMID: 29455764
- PMCID: PMC5903070
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ihj.2017.11.015
Management protocols for chronic heart failure in India
Abstract
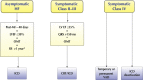
Heart failure is a common clinical syndrome and a global health priority. The burden of heart failure is increasing at an alarming rate worldwide as well as in India. Heart failure not only increases the risk of mortality, morbidity and worsens the patient's quality of life, but also puts a huge burden on the overall healthcare system. The management of heart failure has evolved over the years with the advent of new drugs and devices. This document has been developed with an objective to provide standard management guidance and simple heart failure algorithms to aid Indian clinicians in their daily practice. It would also inform the clinicians on the latest evidence in heart failure and provide guidance to recognize and diagnose chronic heart failure early and optimize management.
Keywords: Algorithms; CHF; Chronic heart failure; Devices; Diagnosis; Drugs; HF; Heart failure; India; Management standards; Practice guidance; Protocols; Treatment.
Copyright © 2017. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures

References
-
- Ponikowski P. Heart failure: preventing disease and death worldwide. ESC Heart Fail. 2014;1:4–25. - PubMed
-
- Ambrosy A.P. The global health and economic burden of hospitalizations for heart failure: lessons learned from hospitalized heart failure registries. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63:1123–1133. - PubMed
-
- Joyce E. Variable contribution of heart failure to quality of life in ambulatory heart failure with reduced, better, or preserved ejection fraction. JACC Heart Fail. 2016;4:184–193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

