Hopanoid lipids: from membranes to plant-bacteria interactions
- PMID: 29456243
- PMCID: PMC6087623
- DOI: 10.1038/nrmicro.2017.173
Hopanoid lipids: from membranes to plant-bacteria interactions
Abstract
Lipid research represents a frontier for microbiology, as showcased by hopanoid lipids. Hopanoids, which resemble sterols and are found in the membranes of diverse bacteria, have left an extensive molecular fossil record. They were first discovered by petroleum geologists. Today, hopanoid-producing bacteria remain abundant in various ecosystems, such as the rhizosphere. Recently, great progress has been made in our understanding of hopanoid biosynthesis, facilitated in part by technical advances in lipid identification and quantification. A variety of genetically tractable, hopanoid-producing bacteria have been cultured, and tools to manipulate hopanoid biosynthesis and detect hopanoids are improving. However, we still have much to learn regarding how hopanoid production is regulated, how hopanoids act biophysically and biochemically, and how their production affects bacterial interactions with other organisms, such as plants. The study of hopanoids thus offers rich opportunities for discovery.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


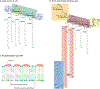
References
-
- Brocks JJ & Banfield J Biomarker evidence for green and purple sulphur bacteria in a stratified Paleoproterozoic sea. Nature 437, 866–870 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Ourisson G & Albrecht P Geohopanoids: the most abundant natural products on Earth? Acc. Chem. Res 25, 398–402 (1992).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

