Correlative analysis of plasma and urine neopterin levels in the pre- and post-menopausal women with periodontitis, following nonsurgical periodontal therapy
- PMID: 29456301
- PMCID: PMC5813341
- DOI: 10.4103/jisp.jisp_278_17
Correlative analysis of plasma and urine neopterin levels in the pre- and post-menopausal women with periodontitis, following nonsurgical periodontal therapy
Abstract
Context: Periodontitis is an inflammatory condition which is distinguished by the devastation of the supported tooth structures. In such inflammatory conditions, some biomarkers such as neopterin will be secreted and elevated in the body fluids, which can be used as a diagnostic marker for the present and future disease activity.
Aims: Assessment of the neopterin as a biomarker in inflammatory conditions such as menopause and periodontitis.
Settings and design: A cross-sectional interventional study.
Materials and methods: Sixty female individuals with a mean age of 40-60 years with chronic periodontitis were included in this study. All were categorized into two groups of thirty each, depending on their menstrual history: Group I - thirty premenopausal women and Group II - thirty postmenopausal women. Urine and plasma were collected from both groups to estimate neopterin levels. ELISA kit was used to assess the neopterin levels at baseline and after 3 months of nonsurgical periodontal therapy (NSPT).
Statistical analysis used: IBM SPSS version 21 software.
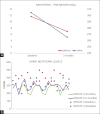
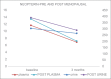
Results: A significant depreciation in the mean values of all the parameters from baseline to 3 months (P < 0.001), in the intragroup analysis, was observed. Plasma (0.006) and urine (0.004) reduction was seen.
Conclusions: In both the groups, in 3 months after NSPT, decreased neopterin levels were found, suggesting that the NSPT is the definitive therapy. Further, suggesting that, neopterin levels in the plasma and urine can be used as an index to identify the periodontal inflammation and destruction.
Keywords: Menopause; neopterin; nonsurgical periodontal therapy; periodontitis; scaling and root planing.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- de Queiroz AC, Taba M, Jr, O’Connell PA, da Nóbrega PB, Costa PP, Kawata VK, et al. Inflammation markers in healthy and periodontitis patients: A preliminary data screening. Braz Dent J. 2008;19:3–8. - PubMed
-
- Zhang L, Henson BS, Camargo PM, Wong DT. The clinical value of salivary biomarkers for periodontal disease. Periodontol 2000. 2009;51:25–37. - PubMed
-
- Chapple IL. Periodontal diagnosis and treatment – Where does the future lie? Periodontol 2000. 2009;51:9–24. - PubMed
-
- Marsálek P, Svoboda M, Smutná M, Blahová J, Vecerek V. Neopterin and biopterin as biomarkers of immune system activation associated with castration in piglets. J Anim Sci. 2011;89:1758–62. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

