Clinical Approaches to Breast Reconstruction: What Is the Appropriate Reconstructive Procedure for My Patient?
- PMID: 29456467
- PMCID: PMC5803680
- DOI: 10.1159/000484926
Clinical Approaches to Breast Reconstruction: What Is the Appropriate Reconstructive Procedure for My Patient?
Abstract
Breast reconstruction after breast cancer is an emotional subject for women. Consequently, the correct timing and surgical procedure for each individual woman are important. In general, heterologous or autologous reconstructive procedures are available, both having advantages and disadvantages. Breast size, patient habitus, and previous surgeries or radiation therapy need to be considered, independent of the chosen procedure. New surgical techniques, refinement of surgical procedures, and the development of supportive materials have increased the general patient collective eligible for breast reconstruction. This review highlights the different approaches to immediate breast reconstruction using autologous or heterologous techniques.
Keywords: Acellular dermal matrix; Autologous breast reconstruction; Breast reconstruction; Heterologous breast reconstruction; Mesh.
Figures

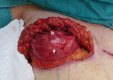

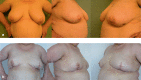


References
-
- RKI, Robert-Koch-Institut Evaluation of Cancer Incidence in Germany (2007–2010). www.rki.de/DE/Home/homepage_node.html; last accessed on 5 August 2017.
-
- Romics L, Chew BK, Weiler-Mithoff E, et al. Ten-year follow-up of skin-sparing mastectomy followed by immediate breast reconstruction. Br J Surg. 2012;99:799–806. - PubMed
-
- Mallon P, Feron JG, Couturaud B, et al. The role of nipple-sparing mastectomy in breast cancer: a comprehensive review of the literature. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;131:969–984. - PubMed
-
- Gerber B, Krause A, Dieterich M, et al. The oncological safety of skin sparing mastectomy with conservation of the nipple-areola complex and autologous reconstruction: an extended follow-up study. Ann Surg. 2009;249:461–468. - PubMed
-
- Kronowitz SJ, Robb GL. Radiation therapy and breast reconstruction: a critical review of the literature. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;124:395–408. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

