A Novel Missense Variant in the PVRL4 Gene Underlying Ectodermal Dysplasia-Syndactyly Syndrome in a Turkish Child
- PMID: 29456479
- PMCID: PMC5803726
- DOI: 10.1159/000479359
A Novel Missense Variant in the PVRL4 Gene Underlying Ectodermal Dysplasia-Syndactyly Syndrome in a Turkish Child
Abstract
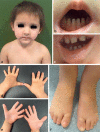
Ectodermal dysplasia-syndactyly syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive congenital disorder caused by mutations in PVRL4 coding for nectin-4. Five different mutations in the PVRL4 gene, including 3 homozygous missense mutations, have been reported. Here, we present an unreported missense variant (c.247C>T, p.His83Tyr) in a consanguineous Turkish family.
Keywords: Ectodermal dysplasia; PVRL4; Syndactyly.
Figures
References
-
- Brancati F, Agolini E, Fortugno P. Nectinopathies: an emerging group of ectodermal dysplasia syndromes. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2013;148:59–64. - PubMed
-
- Fortugno P, Josselin E, Tsiakas K, Agolini E, Cestra G, et al. Nectin-4 mutations causing ectodermal dysplasia with syndactyly perturb the Rac1 pathway and the kinetics of adherens junction formation. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:2146–2153. - PubMed
-
- Freire-Maia N. Ectodermal dysplasias. Hum Hered. 1971;21:309–312. - PubMed
-
- Jelani M, Chishti MS, Ahmad W. Mutation in PVRL4 gene encoding nectin-4 underlies ectodermal-dysplasia-syndactyly syndrome (EDSS1) J Hum Genet. 2011;56:352–357. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources