SMO Inhibition Modulates Cellular Plasticity and Invasiveness in Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 29456503
- PMCID: PMC5801594
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00956
SMO Inhibition Modulates Cellular Plasticity and Invasiveness in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
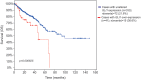
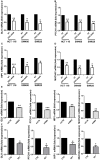
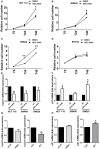
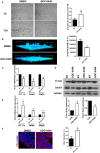
HIGHLIGHTS Preliminary results of this work were presented at the 2016 Academic Surgical Congress, Jacksonville (FL), February 2-4 2016 (Original title: Selective Smo-Inhibition Interferes With Cellular Energetic Metabolism In Colorectal Cancer)This study was funded by "Sapienza-University of Rome" (Funds for young researchers) and "AIRC" (Italian Association for Cancer Research)Hedgehog inhibitor was kindly provided by Genentech, Inc.®. Colon Cancer (CC) is the fourth most frequently diagnosed tumor and the second leading cause of death in the USA. Abnormalities of Hedgehog pathway have been demonstrated in several types of human cancers, however the role of Hedgehog (Hh) in CC remain controversial. In this study, we analyzed the association between increased mRNA expression of GLI1 and GLI2, two Hh target genes, and CC survival and recurrence by gene expression microarray from a cohort of 382 CC patients. We found that patients with increased expression of GLI1 showed a statistically significant reduction in survival. In order to demonstrate a causal role of Hh pathway activation in the pathogenesis of CC, we treated HCT 116, SW480 and SW620 CC cells lines with GDC-0449, a pharmacological inhibitor of Smoothened (SMO). Treatment with GDC-0449 markedly reduced expression of Hh target genes GLI1, PTCH1, HIP1, MUC5AC, thus indicating that this pathway is constitutively active in CC cell lines. Moreover, GDC-0449 partially reduced cell proliferation, which was associated with upregulation of p21 and downregulation of CycD1. Finally, treatment with the same drug reduced migration and three-dimensional invasion, which were associated with downregulation of Snail1, the EMT master gene, and with induction of the epithelial markers Cytokeratin-18 and E-cadherin. These results were confirmed by SMO genetic silencing. Notably, treatment with 5E1, a Sonic Hedgehog-specific mAb, markedly reduced the expression of Hedgehog target genes, as well as inhibited cell proliferation and mediated reversion toward an epithelial phenotype. This suggests the existence of a Hedgehog autocrine signaling loop affecting cell plasticity and fostering cell proliferation and migration/invasion in CC cell lines. These discoveries encourage future investigations to better characterize the role of Hedgehog in cellular plasticity and invasion during the different steps of CC pathogenesis.
Keywords: EMT; SMO inhibition; cell invasiveness; cell plasticity; colon cancer; hedgehog pathway.
Figures
References
-
- Battistelli C., Cicchini C., Santangelo L., Tramontano A., Grassi L., Gonzalez F. J., et al. (2017). The Snail repressor recruits EZH2 to specific genomic sites through the enrollment of the lncRNA HOTAIR in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Oncogene 36, 942–955. 10.1038/onc.2016.260 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benvenuto M., Masuelli L., De Smaele E., Fantini M., Mattera R., Cucchi D., et al. (2016). In vitro and in vivo inhibition of breast cancer cell growth by targeting the Hedgehog/GLI pathway with SMO (GDC-0449) or GLI (GANT-61) inhibitors. Oncotarget 7, 9250–9270. 10.18632/oncotarget.7062 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

