A Review on Central Nervous System Effects of Gastrodin
- PMID: 29456504
- PMCID: PMC5801292
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00024
A Review on Central Nervous System Effects of Gastrodin
Abstract
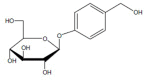
Rhizoma Gastrodiae (also known as Tian ma), the dried rhizome of Gastrodia elata Blume, is a famous Chinese herb that has been traditionally used for the treatment of headache, dizziness, spasm, epilepsy, stoke, amnesia and other disorders for centuries. Gastrodin, a phenolic glycoside, is the main bioactive constituent of Rhizoma Gastrodiae. Since identified in 1978, gastrodin has been extensively investigated on its pharmacological properties. In this article, we reviewed the central nervous system (CNS) effects of gastrodin in preclinical models of CNS disorders including epilepsy, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, affective disorders, cerebral ischemia/reperfusion, cognitive impairment as well as the underlying mechanisms involved and, where possible, clinical data that support the pharmacological activities. The sources and pharmacokinetics of gastrodin were also reviewed here. As a result, gastrodin possesses a broad range of beneficial effects on the above-mentioned CNS diseases, and the mechanisms of actions include modulating neurotransmitters, antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, suppressing microglial activation, regulating mitochondrial cascades, up-regulating neurotrophins, etc. However, more detailed clinical trials are still in need for positioning it in the treatment of neurological disorders.
Keywords: Chinese medicine; Gastrodia; Gastrodia elata Blume; central nervous system disorders; pharmacokinetics; pharmacology.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials