Minocycline through attenuation of oxidative stress and inflammatory response reduces the neuropathic pain in a rat model of chronic constriction injury
- PMID: 29456810
- PMCID: PMC5811752
- DOI: 10.22038/IJBMS.2017.24248.6053
Minocycline through attenuation of oxidative stress and inflammatory response reduces the neuropathic pain in a rat model of chronic constriction injury
Abstract
Objectives: Several lines of evidence showed that minocycline possesses antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. This study aimed to demonstrate the effects of minocycline in rats subjected to chronic constriction injury (CCI).
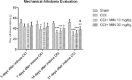
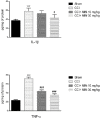
Materials and methods: In this study four groups (n = 6-8) of rats were used as follows: Sham, CCI, CCI + minocycline (MIN) 10 mg/Kg (IP) and CCI + MIN 30 mg/Kg (IP). On days 3, 7, 14, and 21 post-surgery hot-plate, acetone, and von Frey tests were carried out. Finally, Motor Nerve Conduction Velocity Evaluation (MNCV) assessment was performed and spinal cords were harvested in order to measure tissue concentrations of TNF_α, IL-1β, Glutathione peroxidase (GPx), Superoxide dismutase (SOD) and Malondialdehyde (MDA). Extent of perineural inflammation and damage around the sciatic nerve was histopathologically evaluated.
Results: Our results demonstrated that CCI significantly caused hyperalgesia and allodynia twenty-one days after CCI. MIN attenuated heat hyperalgesia, cold and mechanical allodynia and MNCV in animals. MIN also decreased the levels of TNF_α and IL-1β. Antioxidative enzymes (SOD, MDA, and GPx) were restored following MIN treatment. Our findings showed that MIN decreased perineural inflammation around the sciatic nerve. According to the results, the neuropathic pain reduced in the CCI hyperalgesia model using 30 mg/kg of minocycline.
Conclusion: It is suggested that antinociceptive effects of minocycline might be mediated through the inhibition of inflammatory response and attenuation of oxidative stress.
Keywords: Chronic constriction; Inflammatory response; Injury; Minocycline; Neuropathic pain; Oxidative stress; Rat.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The Antinociceptive Effects of Combined Treatment With Atorvastatin and Vitamin C in the Chronic Constriction Injury Model of Rats.Basic Clin Neurosci. 2023 Nov-Dec;14(6):727-739. doi: 10.32598/bcn.2022.895.2. Epub 2023 Nov 1. Basic Clin Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 39070196 Free PMC article.
-
The Antinociceptive Effects of Rosuvastatin in Chronic Constriction Injury Model of Male Rats.Basic Clin Neurosci. 2018 Jul-Aug;9(4):251-260. doi: 10.32598/bcn.9.4.251. Epub 2018 Jul 1. Basic Clin Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30519383 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Effects of Probiotic Supplementation on Neuropathic Pain and Oxidative Stress Factors in an Animal Model of Chronic Constriction Injury of the Sciatic Nerve.Basic Clin Neurosci. 2023 May-Jun;14(3):375-384. doi: 10.32598/bcn.2022.3772.1. Epub 2023 May 1. Basic Clin Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38077171 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective effect of l-theanine in a rat model of chronic constriction injury of sciatic nerve-induced neuropathic pain.J Formos Med Assoc. 2022 Apr;121(4):802-814. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2021.08.023. Epub 2021 Sep 13. J Formos Med Assoc. 2022. PMID: 34531102
-
Hyperbaric oxygenation therapy alleviates chronic constrictive injury-induced neuropathic pain and reduces tumor necrosis factor-alpha production.Anesth Analg. 2011 Sep;113(3):626-33. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e31821f9544. Epub 2011 May 19. Anesth Analg. 2011. PMID: 21596875
Cited by
-
1,3,4-Oxadiazole Derivative Attenuates Chronic Constriction Injury Induced Neuropathic Pain: A Computational, Behavioral, and Molecular Approach.Brain Sci. 2020 Oct 13;10(10):731. doi: 10.3390/brainsci10100731. Brain Sci. 2020. PMID: 33066162 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring gene signatures and regulatory networks in a rat model of sciatica: implications and validation in neuropathic pain.Front Mol Neurosci. 2024 Feb 6;16:1261217. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1261217. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38379852 Free PMC article.
-
The Molecular Mechanism of Aluminum Phosphide poisoning in Cardiovascular Disease: Pathophysiology and Diagnostic Approach.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2020 Oct;20(5):454-461. doi: 10.1007/s12012-020-09592-4. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32712815 Review.
-
The effects of maternal separation stress experienced by parents on male reproductive potential in the next generation.Heliyon. 2020 Sep 29;6(9):e04807. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04807. eCollection 2020 Sep. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 33024852 Free PMC article.
-
Photobiomodulation and B vitamins administration produces antinociception in an orofacial pain model through the modulation of glial cells and cytokines expression.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2020 Jan 26;2:100040. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2020.100040. eCollection 2020 Feb. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2020. PMID: 34589831 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dworkin RH, Backonja M, Rowbotham MC, Allen RR, Argoff CR, Bennett GJ, et al. Advances in neuropathic pain: diagnosis, mechanisms, and treatment recommendations. Arch Neurol. 2003;60:1524–1534. - PubMed
-
- De Jongh RF, Vissers KC, Meert TF, Booij LH, De Deyne CS, Heylen RJ. The role of interleukin-6 in nociception and pain. Anesth Analg. 2003;96:1096–1103. - PubMed
-
- Saika F, Kiguchi N, Kobayashi Y, Kishioka S. Peripheral alpha4beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor signalling attenuates tactile allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia after nerve injury in mice. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2015;213:462–471. - PubMed
-
- Ma W, Quirion R. Does COX2-dependent PGE2 play a role in neuropathic pain?Neurosci Lett. 2008;437:165–169. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
