The Effect of Levothyroxine and Selenium versus Levothyroxine Alone on Reducing the Level of Anti-thyroid Peroxidase Antibody in Autoimmune Hypothyroid Patients
- PMID: 29456972
- PMCID: PMC5812089
- DOI: 10.4103/2277-9175.223735
The Effect of Levothyroxine and Selenium versus Levothyroxine Alone on Reducing the Level of Anti-thyroid Peroxidase Antibody in Autoimmune Hypothyroid Patients
Abstract
Background: Due to the prevalence of autoimmune hypothyroidism and its effects on physical and mental health it is necessary to provide a treatment which is also effective in preventing the progression of sub-clinical hypothyroidism in these patients. This study aims to investigate the effect of selenium supplementation on of anti-thyroid hormone antibodies in these patients.
Materials and methods: In a randomized clinical trial, 70 patients with autoimmune hypothyroidism randomly divided into two groups of 35 each, the first group was treated with oral selenium treatment with levothyroxine (LT4) and to the second group along with LT4, placebo was also prescribed. Serum selenium level, thyroid hormones and anti-thyroid hormone antibodies before and after 3 months of treatment in both groups, were determined, and the results were analyzed using SPSS software.
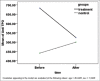
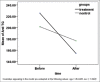
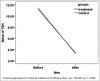
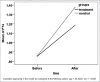
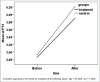
Results: The mean of the serum anti-thyroid peroxidase serum level in the intervention group before and after treatment was 682.18 ± 87.25 and 522.96 ± 47.21 and the difference before and after treatment was statistically significant (P = 0.021). The level of this antibody before and after treatment in the control group was 441 ± 53.54 and 501.18 ± 77.68, and no significant differences between two groups were observed before and after treatment (P = 0.42).
Conclusion: Selenium supplementation may help to reduce the levels of antibodies in patients with autoimmune hypothyroidism.
Keywords: Anti-thyroid hormone antibodies; autoimmune hypothyroidism; selenium.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Baretic M. 100 years of Hashimoto thyroiditis, still an intriguing disease. Acta Med Croatica. 2011;65:453–7. - PubMed
-
- Fink H, Hintze G. Autoimmune thyroiditis (Hashimoto's thyroiditis): Current diagnostics and therapy. Med Klin (Munich) 2010;105:485–93. - PubMed
-
- Trbojevic B, Djurica S. Diagnosis of autoimmune thyroid disease. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2005;133(Suppl 1):25–33. - PubMed
-
- Schomburg L. Selenium, selenoproteins and the thyroid gland: Interactions in health and disease. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2011;8:160–71. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

