Quercetin Prevents Body Weight Loss Due to the Using of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in Rat
- PMID: 29456979
- PMCID: PMC5812102
- DOI: 10.4103/abr.abr_141_17
Quercetin Prevents Body Weight Loss Due to the Using of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in Rat
Abstract
Background: Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPION) have been largely considered for numerous applications in biomedicine such as magnetic resonance imaging, hyperthermia, cell tracking, anticancer treatment, and targeted delivery of drugs or genes. However, they may have side effects such body weight loss. Quercetin (QT), a strong antioxidant and free radical scavenger and a natural flavonoid, has a wide range of biological and therapeutic effects. In this study, the effect of QT on prevention of weight loss due to the using of SPION has been investigated.
Materials and methods: SPION and QT-SPION were administered orally at 50 and 100 mg/kg for 7 days. Then, the body weight was measured at the beginning and the end of the study.
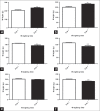
Results: Rats fed with 50 and 100 mg/kg SPION showed a significant weight loss, whereas those that fed with 50 mg/kg QT-SPION did not. A weight loss was observed in rats treated with 100 mg/kg of QT-SPION.
Conclusions: The results of this study showed that quercetin could prevent weight loss due to the SPION.
Keywords: Nanoparticles; quercetin; superparamagnetic iron oxide; weight loss.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kumari A, Yadav SK, Pakade YB, Singh B, Yadav SC. Development of biodegradable nanoparticles for delivery of quercetin. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2010;80:184–92. - PubMed
-
- Wu TH, Yen FL, Lin LT, Tsai TR, Lin CC, Cham TM, et al. Preparation, physicochemical characterization, and antioxidant effects of quercetin nanoparticles. Int J Pharm. 2008;346:160–8. - PubMed
-
- Manach C, Scalbert A, Morand C, Rémésy C, Jiménez L. Polyphenols: Food sources and bioavailability. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;79:727–47. - PubMed
-
- Chakraborty S, Stalin S, Das N, Choudhury ST, Ghosh S, Swarnakar S, et al. The use of nano-quercetin to arrest mitochondrial damage and MMP-9 upregulation during prevention of gastric inflammation induced by ethanol in rat. Biomaterials. 2012;33:2991–3001. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

