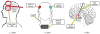A review of brain stimulation methods to treat substance use disorders
- PMID: 29457674
- PMCID: PMC6034717
- DOI: 10.1111/ajad.12674
A review of brain stimulation methods to treat substance use disorders
Abstract
Background: Substance use disorders (SUDs) are a leading cause of disability worldwide. While several pharmacological and behavioral treatments for SUDs are available, these may not be effective for all patients. Recent studies using non-invasive neuromodulation techniques including Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS), Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS), and Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) have shown promise for SUD treatment.
Objective: Multiple studies were evaluated investigating the therapeutic potential of non-invasive brain stimulation techniques in treatment of SUDs.
Method: Through literature searches (eg, PubMed, Google Scholar), 60 studies (2000-2017) were identified examining the effect of rTMS, tDCS, or DBS on cravings and consumption of SUDs, including tobacco, alcohol, cannabis, opioids, and stimulants.
Results: rTMS and tDCS demonstrated decreases in drug craving and consumption, while early studies with DBS suggest similar results. Results are most encouraging when stimulation is targeted to the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex (DLPFC).
Conclusions: Short-term treatment with rTMS and tDCS may have beneficial effects on drug craving and consumption. Future studies should focus on extending therapeutic benefits by increasing stimulation frequency and duration of treatment.
Scientific significance: The utility of these methods in SUD treatment and prevention are unclear, and warrants further study using randomized, controlled designs. (Am J Addict 2018;27:71-91).
Keywords: Alcohol; Brain Stimulation; Cannabis; Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS); Non-Invasive; Opioids; Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS); Stimulants; Tobacco; Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS).
© 2018 American Academy of Addiction Psychiatry.
Figures
References
-
- Facing Addiction in America: The Surgeon General’s Report on Alcohol, Drugs, and Health. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS); Washington, DC: 2016. - PubMed
-
- World Drug Report 2014. Vienna: United Nations Publication; 2014.
-
- Wing VC, Barr MS, Wass CE, et al. Brain stimulation methods to treat tobacco addiction. Brain Stimul. 2013;6:221–230. - PubMed
-
- Barr MS, Farzan F, Wing VC, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation and drug addiction. Int Rev Psychiatry (Abingdon, England) 2011;23:454–466. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical