A quantitative trait locus on chromosome 1 modulates intermale aggression in mice
- PMID: 29457871
- PMCID: PMC6098989
- DOI: 10.1111/gbb.12469
A quantitative trait locus on chromosome 1 modulates intermale aggression in mice
Abstract
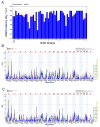
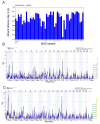
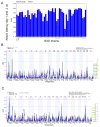
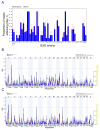
Aggression between male conspecifics is a complex social behavior that is likely modulated by multiple gene variants. In this study, the BXD recombinant inbred mouse strains (RIS) were used to map quantitative trait loci (QTLs) underlying behaviors associated with intermale aggression. Four hundred and fifty-seven males from 55 strains (including the parentals) were observed at an age of 13 ± 1 week in a resident-intruder test following 10 days of isolation. Attack latency was measured directly within a 10-minute time period and the test was repeated 24 hours later. The variables we analyzed were the proportion of attacking males in a given strain as well as the attack latency (on days 1 and 2, and both days combined). On day 1, 29% of males attacked, and this increased to 37% on day 2. Large strain differences were obtained for all measures of aggression, indicating substantial heritability (intraclass correlations 0.10-0.18). We identified a significant QTL on chromosome (Chr) 1 and suggestive QTLs on mouse Chrs 1 and 12 for both attack and latency variables. The significant Chr 1 locus maps to a gene-sparse region between 82 and 88.5 Mb with the C57BL/6J allele increasing aggression and explaining about 18% of the variance. The most likely candidate gene modulating this trait is Htr2b which encodes the serotonin 2B receptor and has been implicated in aggressive and impulsive behavior in mice, humans and other species.
Keywords: Ht2rb; aggression; anxiety; attack latency; impulsive behavior; mouse; recombinant inbred strains; resident-intruder; serotonin; social behavior.
© 2018 John Wiley & Sons Ltd and International Behavioural and Neural Genetics Society.
Figures
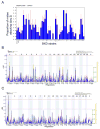
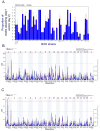
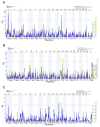
Similar articles
-
Mapping of Genetic Factors That Elicit Intermale Aggressive Behavior on Mouse Chromosome 15: Intruder Effects and the Complex Genetic Basis.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 21;10(9):e0137764. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137764. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26389588 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative trait locus analysis of aggressive behaviours in mice.Novartis Found Symp. 2005;268:57-69; discussion 69-77, 96-9. Novartis Found Symp. 2005. PMID: 16206875 Review.
-
Genomic mapping of social behavior traits in a F2 cross derived from mice selectively bred for high aggression.BMC Genet. 2010 Dec 31;11:113. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-11-113. BMC Genet. 2010. PMID: 21194443 Free PMC article.
-
Attack behaviors in mice: from factorial structure to quantitative trait loci mapping.Eur J Pharmacol. 2005 Dec 5;526(1-3):172-85. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.09.026. Epub 2005 Nov 2. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16266699 Review.
-
A QTL on Chr 5 modifies hearing loss associated with the fascin-2 variant of DBA/2J mice.Mamm Genome. 2015 Aug;26(7-8):338-47. doi: 10.1007/s00335-015-9574-y. Epub 2015 Jun 20. Mamm Genome. 2015. PMID: 26092689 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of kinship correction on inflation of genetic interaction statistics in commonly used mouse populations.G3 (Bethesda). 2021 Jul 14;11(7):jkab131. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkab131. G3 (Bethesda). 2021. PMID: 33892506 Free PMC article.
-
The Implication of 5-HT Receptor Family Members in Aggression, Depression and Suicide: Similarity and Difference.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 8;23(15):8814. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158814. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Male and female behavioral variability and morphine response in C57BL/6J, DBA/2J, and their BXD progeny following chronic stress exposure.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 28;14(1):30785. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-80767-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39730457 Free PMC article.
-
Connectivity and molecular profiles of Foxp2- and Dbx1-lineage neurons in the accessory olfactory bulb and medial amygdala.J Comp Neurol. 2024 Feb;532(2):e25545. doi: 10.1002/cne.25545. Epub 2023 Oct 17. J Comp Neurol. 2024. PMID: 37849047 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bennett B, Carosone-Link P, Zahniser NR, Johnson TE. Confirmation and fine mapping of ethanol sensitivity quantitative trait loci, and candidate gene testing in the LXS recombinant inbred mice. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 2006;319:299–307. - PubMed
-
- Bevilacqua L, Doly S, Kaprio J, Yuan Q, Tikkanen R, Paunio T, Zhou Z, Wedenoja J, Maroteaux L, Diaz S, Belmer A, Hodgkinson CA, Dell’osso L, Suvisaari J, Coccaro E, Rose RJ, Peltonen L, Virkkunen M, Goldman D. A population-specific HTR2B stop codon predisposes to severe impulsivity. Nature. 2010;468:1061–1066. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brain PF. Differentiating types of attack and defense in rodents. In: Brain PF, Benton D, editors. Multidisciplinary Approaches to Aggression Research. Elsevier North-Holland Biomedical Press; 1981. pp. 53–71.
-
- Brain PF, Childs G, Parmigiani S. Videotape analysis of different forms of murine aggression. Neurosci Lett. 1991:1–3.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

