Human regulatory proteins associate with non-coding RNAs from the EBV IR1 region
- PMID: 29458410
- PMCID: PMC5819218
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-018-3250-8
Human regulatory proteins associate with non-coding RNAs from the EBV IR1 region
Abstract
Objective: The function of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) stable intronic sequence (sis)RNAs, non-coding RNAs transcribed from a region required for EBV-mediated cellular transformation, remain unknown. To better understand the function of ebv-sisRNA-1 and ebv-sisRNA-2 from the internal repeat (IR)1 region of EBV, we used a combination of bioinformatics and biochemistry to identify associated RNA binding proteins. The findings reported here are part of ongoing studies to determine the functions of non-coding RNAs from the IR1 region of EBV.
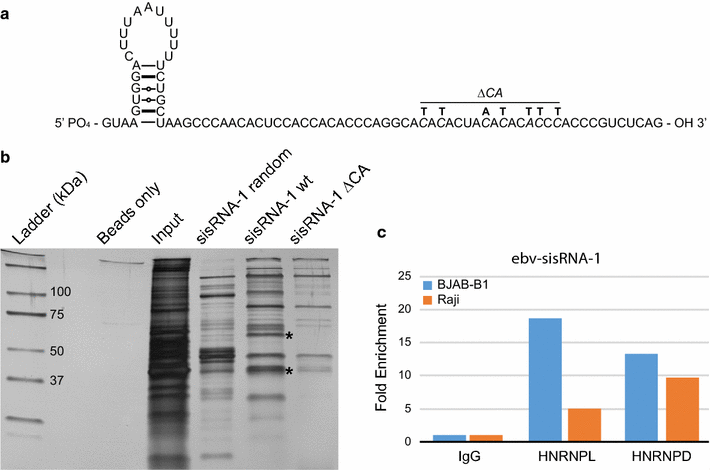
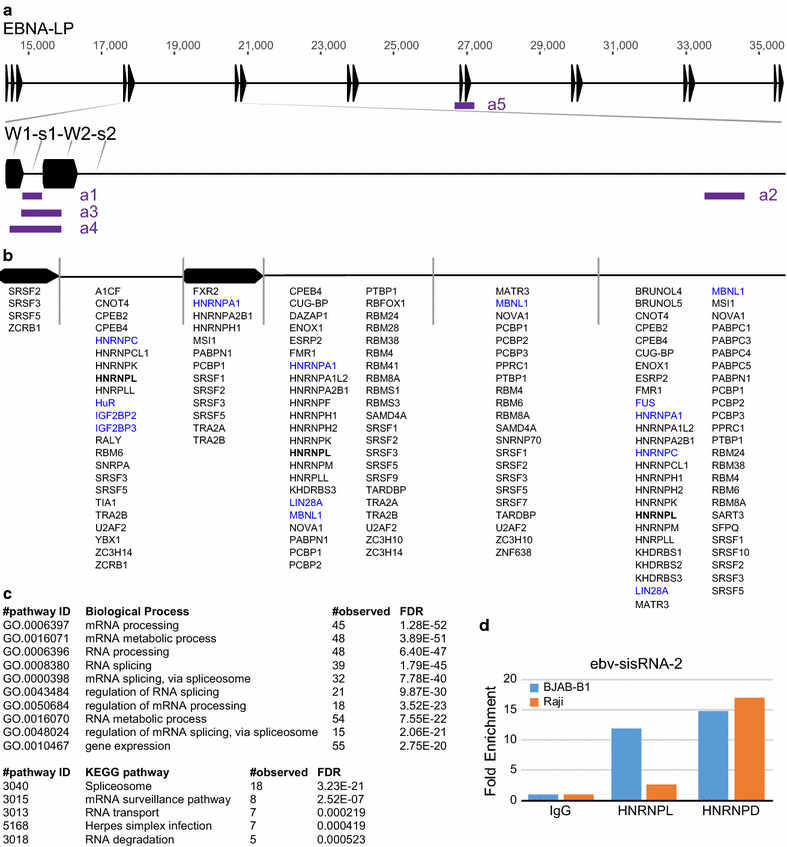
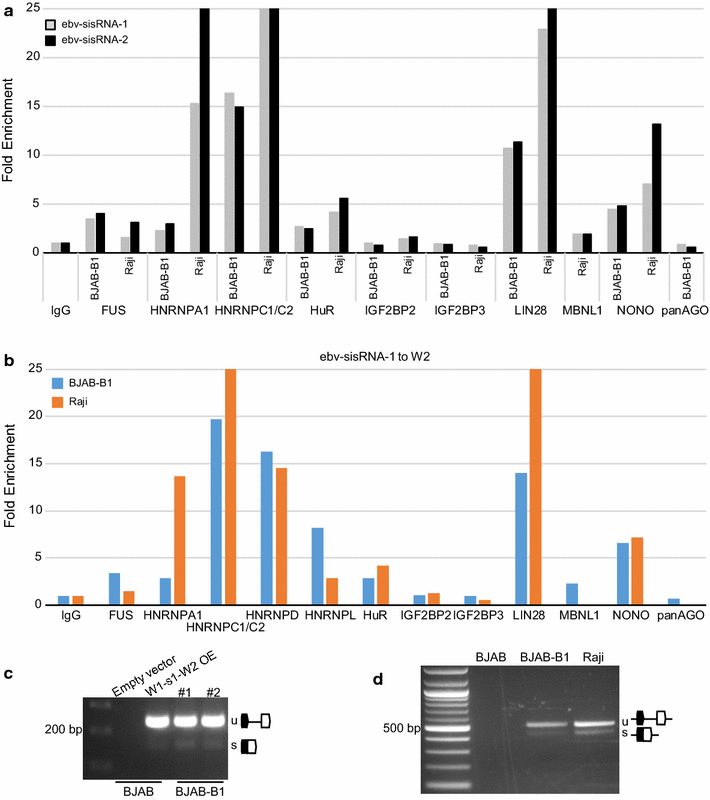
Results: Human regulatory proteins HNRNPA1 (heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1), HNRNPC, HNRNPL, HuR (human antigen R), and protein LIN28A (lin-28 homolog A) were predicted to bind ebv-sisRNA-1 and/or ebv-sisRNA-2; FUS (fused in sarcoma) was predicted to associate with ebv-sisRNA-2. Protein interactions were validated using a combination of RNA immunoprecipitation and biotin pulldown assays. Both sisRNAs also precipitated with HNRNPD and NONO (non-POU domain-containing octamer-binding protein). Interestingly, each of these interacting proteins also precipitated non-spliced non-coding RNA sequences transcribed from the IR1 region. Our findings suggest interesting roles for sisRNAs (through their interactions with regulatory proteins) and provide further evidence for the existence of non-spliced stable non-coding RNAs.
Keywords: EBNA-LP; EBV; FUS; HNRNP; HuR; IR1; LIN28; NONO; lncRNA; ncRNA; sisRNA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of a structured intronic region of the LMP2 pre-mRNA from EBV reveals associations with human regulatory proteins and nuclear actin.BMC Res Notes. 2019 Jan 18;12(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s13104-019-4070-1. BMC Res Notes. 2019. PMID: 30658689 Free PMC article.
-
Host Gene Expression Is Regulated by Two Types of Noncoding RNAs Transcribed from the Epstein-Barr Virus BamHI A Rightward Transcript Region.J Virol. 2015 Nov;89(22):11256-68. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01492-15. Epub 2015 Aug 26. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26311882 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analyses of Epstein-Barr virus reveal conserved RNA structures and a novel stable intronic sequence RNA.BMC Genomics. 2013 Aug 9;14:543. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-543. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23937650 Free PMC article.
-
RNA families in Epstein-Barr virus.RNA Biol. 2014;11(1):10-7. doi: 10.4161/rna.27488. Epub 2013 Dec 20. RNA Biol. 2014. PMID: 24441309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifunctional non-coding Epstein-Barr virus encoded RNAs (EBERs) contribute to viral pathogenesis.Virus Res. 2016 Jan 2;212:30-8. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2015.08.007. Epub 2015 Aug 18. Virus Res. 2016. PMID: 26292159 Review.
Cited by
-
A survey of RNA secondary structural propensity encoded within human herpesvirus genomes: global comparisons and local motifs.PeerJ. 2020 Sep 10;8:e9882. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9882. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 32974099 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNAs in Epstein-Barr virus-related cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 May 25;21(1):278. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-01986-w. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 34034760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The many ways Epstein-Barr virus takes advantage of the RNA tool kit.RNA Biol. 2021 May;18(5):759-766. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2021.1875184. Epub 2021 Jan 30. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 33517840 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thermodynamic and structural characterization of an EBV infected B-cell lymphoma transcriptome.NAR Genom Bioinform. 2022 Oct 21;4(4):lqac082. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqac082. eCollection 2022 Dec. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2022. PMID: 36285286 Free PMC article.
-
Viral non-coding RNAs: Stealth strategies in the tug-of-war between humans and herpesviruses.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar;111:135-147. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.06.015. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 32631785 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

