Immunoregulatory functions and the therapeutic implications of GARP-TGF-β in inflammation and cancer
- PMID: 29458436
- PMCID: PMC5819195
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-018-0570-z
Immunoregulatory functions and the therapeutic implications of GARP-TGF-β in inflammation and cancer
Abstract
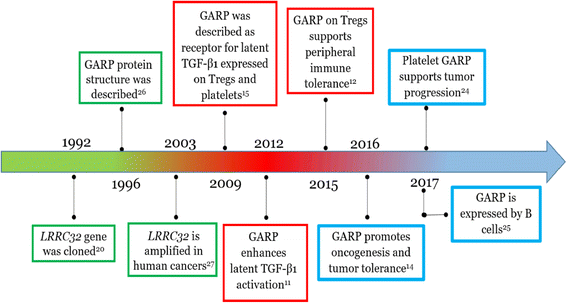
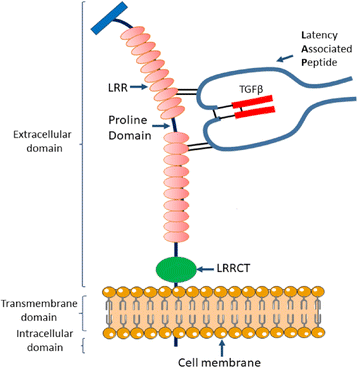
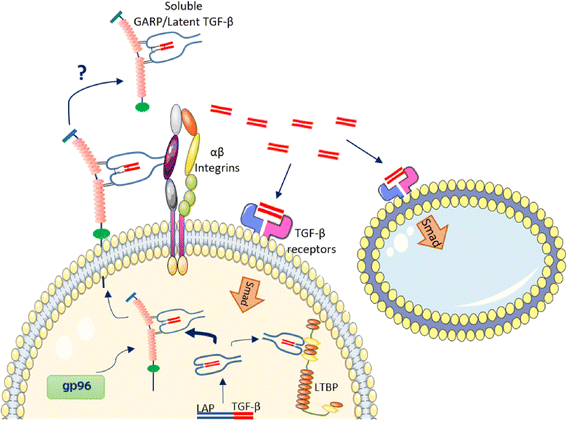
GARP (glycoprotein-A repetitions predominant) is a type I transmembrane cell surface docking receptor for latent transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) that is abundantly expressed on regulatory T lymphocytes and platelets. GARP regulates the availability of membrane-bound latent TGF-β and modulates its activation. For this reason, GARP expression on immune and non-immune cells is involved in maintaining peripheral tolerance. It plays an important role in preventing inflammatory diseases such as allergy and graft versus host disease (GvHD). GARP is also frequently hijacked by cancer cells to promote oncogenesis. This review summarizes the most important features of GARP biology described to date including gene regulation, protein expression and mechanism in activating latent TGF-β, and the function of GARP in regulatory T cell biology and peripheral tolerance, as well as GARP's increasingly recognized roles in platelet-mediated cancer immune evasion. The promise for GARP-targeted strategy as a novel immunotherapy of cancer is also highlighted.
Keywords: Cancer; GARP; Immune tolerance; Platelets; TGF-β; Treg.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This is not applicable for this study.
Consent for publication
The authors have consented fully for the publication of this manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Li MO, Wan YY, Flavell RA. T cell-produced transforming growth factor-beta1 controls T cell tolerance and regulates Th1- and Th17-cell differentiation. Immunity. 2007;26(5):579–591. - PubMed
-
- Gordon KJ, Blobe GC. Role of transforming growth factor-beta superfamily signaling pathways in human disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1782(4):197–228. - PubMed
-
- Li MO, Wan YY, Sanjabi S, Robertson AK, Flavell RA. Transforming growth factor-beta regulation of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:99–146. - PubMed
-
- Zhu HJ, Burgess AW. Regulation of transforming growth factor-beta signaling. Mol Cell Biol Res Commun. 2001;4(6):321–330. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

