Dynamic patterns and predictors of hydroxychloroquine nonadherence among Medicaid beneficiaries with systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 29458974
- PMCID: PMC6035896
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2018.01.002
Dynamic patterns and predictors of hydroxychloroquine nonadherence among Medicaid beneficiaries with systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
Background: Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) is the standard of care medication for most SLE patients, however nonadherence is common. We investigated longitudinal patterns and predictors of nonadherence to HCQ in a U.S. SLE cohort of HCQ initiators.
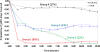
Methods: We used Medicaid data from 28 states to identify adults 18-65 years with prevalent SLE. We included HCQ initiators following ≥6 months without use, and required ≥1 year of follow-up after first dispensing (index date). We used the proportion of days covered (PDC) to describe overall HCQ adherence (<80% = nonadherent) and novel group-based trajectory models (GBTM) to examine monthly patterns (<80% of days/month covered = nonadherent), during the first year of use. Multivariable multinomial logistic regression models were used to examine predictors of nonadherence.
Results: We identified 10,406 HCQ initiators with SLE. Mean age was 38 (±12) years, 94% were female, 42% black, 31% white; 85% had a mean PDC < 80%. In our 4-group GBTM, 17% were persistent adherers, 36% persistent nonadherers, and 47% formed two dynamic patterns of partial adherence. Adherence declined for most patients over the first year. Compared to persistent adherers, the odds of nonadherence were increased for blacks and Hispanics vs. whites and for younger ages vs. older; increased SLE-related comorbidities were associated with reduced odds of nonadherence for persistent nonadherers (0.95, 95% CI: 0.91-0.99).
Conclusions: Among HCQ initiators with SLE, we observed poor adherence which declined for most over the first year of use. HCQ adherence is a dynamic behavior and further studies of associated predictors, outcomes, and interventions should reflect this.
Keywords: Adherence; Health services research; Hydroxychloroquine; Observational study; Pharmacoepidemiology; Systemic lupus erythematosus.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Marengo MF, Waimann CA, de Achaval S, Zhang H, Garcia-Gonzalez A, Richardson MN, et al. Measuring therapeutic adherence in systemic lupus erythematosus with electronic monitoring. Lupus. 2012;21(11):1158–65. - PubMed
-
- A randomized study of the effect of withdrawing hydroxychloroquine sulfate in systemic lupus erythematosus. The Canadian Hydroxychloroquine Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1991;324(3):150–4. - PubMed
-
- Akhavan PS, Su J, Lou W, Gladman DD, Urowitz MB, Fortin PR. The early protective effect of hydroxychloroquine on the risk of cumulative damage in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 2013;40(6):831–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical