Adhesion and relaxation of a soft elastomer on surfaces with skin like roughness
- PMID: 29459289
- PMCID: PMC7617216
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2018.01.032
Adhesion and relaxation of a soft elastomer on surfaces with skin like roughness
Abstract
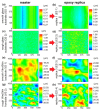
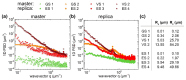
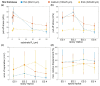
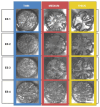
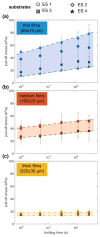
For designing new skin adhesives, the complex mechanical interaction of soft elastomers with surfaces of various roughnesses needs to be better understood. We systematically studied the effects of a wide set of roughness characteristics, film thickness, hold time and material relaxation on the adhesive behaviour of the silicone elastomer SSA 7-9800 (Dow Corning). As model surfaces, we used epoxy replicas obtained from substrates with roughness ranging from very smooth to skin-like. Our results demonstrate that films of thin and intermediate thickness (60 and 160 µm) adhered best to a sub-micron rough surface, with a pull-off stress of about 50 kPa. Significant variations in pull-off stress and detachment mechanism with roughness and hold time were found. In contrast, 320 µm thick films adhered with lower pull-off stress of about 17 kPa, but were less sensitive to roughness and hold time. It is demonstrated that the adhesion performance of the silicone films to rough surfaces can be tuned by tailoring the film thickness and contact time.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Barreau V, Hensel R, Guimard NK, Ghatak A, McMeeking RM, Arzt E. Fibrillar elastomeric micropatterns create tunable adhesion even to rough surfaces. Adv Funct Mater Mater. 2016;26:4687–4694. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201600652. - DOI
-
- Briggs GAD, Briscoe BJ. The effect of surface topography on the adhesion of elastic solids. J Phys D Appl Phys. 1977;10:2453–2466. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/10/18/010. - DOI
-
- Castellanos G, Arzt E, Kamperman M. Effect of viscoelasticity on adhesion of bioinspired micropatterned epoxy surfaces. Langmuir. 2011;27:7752–7759. - PubMed
-
- Chen S, Bhushan B. Nanomechanical and nanotribological characterization of two synthetic skins with and without skin cream treatment using atomic force microscopy. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2013;398:247–254. - PubMed
-
- Dapp WB, Lücke A, Persson BNJ, Müser MH. Self-affine elastic contacts: Percolation and leakage. Phys Rev Lett. 2012;108:1–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

