Inhibition of miR-155 attenuates abdominal aortic aneurysm in mice by regulating macrophage-mediated inflammation
- PMID: 29459426
- PMCID: PMC5938419
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20171432
Inhibition of miR-155 attenuates abdominal aortic aneurysm in mice by regulating macrophage-mediated inflammation
Abstract
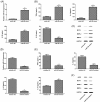
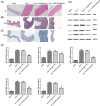
The aim of the present study was to identify abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA)-associated miR-155 contributing to AAA pathology by regulating macrophage-mediated inflammation. Angiotensin II (AngII)-infused apolipoprotein E-deficient (ApoE-/-) mice and THP-1 cells model of miR-155 overexpression and deficiency were used in the experiments. The expression of miR-155 was detected by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Cytokines were evaluated using enzyme-linked immunoabsorbent assay (ELISA). Western blotting was used to measure the levels of MMP-2, MMP-9, iNOS, and monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1 proteins. Immunostaining and transwell were used to determine CD68, elastic collagen, proliferation, and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). The results showed that miR-155 and cytokines were up-regulated in AAA patients or ApoE-/- mice. Overexpression of miR-155 enhanced MMP-2, MMP-9, iNOS, and MCP-1 levels, and stimulated the proliferation and migration of VSMCs. Meanwhile, inhibition of miR-155 had the opposite effect. In addition, histology demonstrated accumulation of CD68 and elastic collagen-positive areas significantly decreased in miR-155 antagomir injection group. In conclusion, the results of the present study suggest that inhibiting miR-155 is crucial to prevent the development of AAA by regulating macrophage inflammation.
Keywords: Abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA); inflammation; macrophage; miR155.
© 2018 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genetic Ablation of MicroRNA-33 Attenuates Inflammation and Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Formation via Several Anti-Inflammatory Pathways.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017 Nov;37(11):2161-2170. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.309768. Epub 2017 Sep 7. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017. PMID: 28882868
-
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm-Associated MicroRNA-516a-5p Regulates Expressions of Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase, Matrix Metalloproteinase-2, and Tissue Inhibitor of Matrix Metalloproteinase-1 in Human Abdominal Aortic Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells.Ann Vasc Surg. 2017 Jul;42:263-273. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2016.10.062. Epub 2017 Mar 10. Ann Vasc Surg. 2017. PMID: 28288890
-
Prevention of abdominal aortic aneurysm by anti-microRNA-712 or anti-microRNA-205 in angiotensin II-infused mice.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Jul;34(7):1412-21. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.303134. Epub 2014 May 8. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 24812324 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2015;13(3):280-90. doi: 10.2174/15701611113119990015. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 23713862 Review.
-
MicroRNA-29b regulation of abdominal aortic aneurysm development.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2014 Jan;24(1):1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2013.05.002. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2014. PMID: 23871588 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of miR‑155‑5p attenuates the valvular damage induced by rheumatic heart disease.Int J Mol Med. 2020 Feb;45(2):429-440. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4420. Epub 2019 Dec 6. Int J Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 31894293 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA CRNDE affects the proliferation and apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells in abdominal aortic aneurysms by regulating the expression of Smad3 by Bcl-3.Cell Cycle. 2020 May;19(9):1036-1047. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1743915. Epub 2020 Apr 2. Cell Cycle. 2020. PMID: 32240036 Free PMC article.
-
The role of miR-155 in cardiovascular diseases: Potential diagnostic and therapeutic targets.Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Risk Prev. 2024 Dec 6;24:200355. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcrp.2024.200355. eCollection 2025 Mar. Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Risk Prev. 2024. PMID: 39760132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNA XIST promotes the proliferation of cardiac fibroblasts and the accumulation of extracellular matrix by sponging microRNA-155-5p.Exp Ther Med. 2021 May;21(5):477. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.9908. Epub 2021 Mar 12. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 33767772 Free PMC article.
-
A review of current status of cell-based therapies for aortic aneurysms.Inflamm Regen. 2023 Aug 7;43(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s41232-023-00280-8. Inflamm Regen. 2023. PMID: 37544997 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Keisler B. and Carter C. (2015) Abdominal aortic aneurysm. Am. Family Physic. 91, 538–543 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

