EGR3 Immediate Early Gene and the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Bipolar Disorder
- PMID: 29459824
- PMCID: PMC5807664
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2018.00015
EGR3 Immediate Early Gene and the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Bipolar Disorder
Abstract
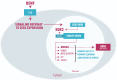
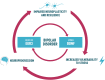
Bipolar disorder (BD) is a severe psychiatric illness with a consistent genetic influence, involving complex interactions between numerous genes and environmental factors. Immediate early genes (IEGs) are activated in the brain in response to environmental stimuli, such as stress. The potential to translate environmental stimuli into long-term changes in brain has led to increased interest in a potential role for these genes influencing risk for psychiatric disorders. Our recent finding using network-based approach has shown that the regulatory unit of early growth response gene 3 (EGR3) of IEGs family was robustly repressed in postmortem prefrontal cortex of BD patients. As a central transcription factor, EGR3 regulates an array of target genes that mediate critical neurobiological processes such as synaptic plasticity, memory and cognition. Considering that EGR3 expression is induced by brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) that has been consistently related to BD pathophysiology, we suggest a link between BDNF and EGR3 and their potential role in BD. A growing body of data from our group and others has shown that peripheral BDNF levels are reduced during mood episodes and also with illness progression. In this same vein, BDNF has been proposed as an important growth factor in the impaired cellular resilience related to BD. Taken together with the fact that EGR3 regulates the expression of the neurotrophin receptor p75NTR and may also indirectly induce BDNF expression, here we propose a feed-forward gene regulatory network involving EGR3 and BDNF and its potential role in BD.
Keywords: bipolar disorder; brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF); early growth response gene 3 (EGR3); immediate early genes; neuroplasticity; regulatory network.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential expression of transcriptional regulatory units in the prefrontal cortex of patients with bipolar disorder: potential role of early growth response gene 3.Transl Psychiatry. 2016 May 10;6(5):e805. doi: 10.1038/tp.2016.78. Transl Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27163206 Free PMC article.
-
The Immediate Early Gene Egr3 Is Required for Hippocampal Induction of Bdnf by Electroconvulsive Stimulation.Front Behav Neurosci. 2018 May 11;12:92. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2018.00092. eCollection 2018. Front Behav Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29867393 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neuroplasticity in bipolar disorder.Expert Rev Neurother. 2008 Jul;8(7):1101-13. doi: 10.1586/14737175.8.7.1101. Expert Rev Neurother. 2008. PMID: 18590480 Review.
-
Serum Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor Levels among Euthymic Adolescents with Bipolar Disorder Type I.Noro Psikiyatr Ars. 2016 Sep;53(3):267-271. doi: 10.5152/npa.2015.8832. Epub 2016 Sep 1. Noro Psikiyatr Ars. 2016. PMID: 28373806 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of BDNF Val66Met polymorphism on cognition in Bipolar Disorder: A review: Special Section on "Translational and Neuroscience Studies in Affective Disorders" Section Editor, Maria Nobile MD, PhD. This Section of JAD focuses on the relevance of translational and neuroscience studies in providing a better understanding of the neural basis of affective disorders. The main aim is to briefly summaries relevant research findings in clinical neuroscience with particular regards to specific innovative topics in mood and anxiety disorders.J Affect Disord. 2019 Jan 15;243:552-558. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2018.07.054. Epub 2018 Jul 24. J Affect Disord. 2019. PMID: 30078664 Review.
Cited by
-
LINC00680 and TTN-AS1 Stabilized by EIF4A3 Promoted Malignant Biological Behaviors of Glioblastoma Cells.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020 Mar 6;19:905-921. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.10.043. Epub 2019 Nov 16. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020. PMID: 32000032 Free PMC article.
-
Serial electroconvulsive Seizure alters dendritic complexity and promotes cellular proliferation in the mouse dentate gyrus; a role for Egr3.Brain Stimul. 2023 May-Jun;16(3):889-900. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2023.04.022. Epub 2023 May 3. Brain Stimul. 2023. PMID: 37146791 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular Signaling Cascades in Bipolar Disorder.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2021;48:101-132. doi: 10.1007/7854_2020_157. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 32860212 Review.
-
Early growth response 1 (EGR1) is downregulated in peripheral blood from patients with major psychiatric disorders.Trends Psychiatry Psychother. 2024 Jan 12;46:e20230749. doi: 10.47626/2237-6089-2023-0749. Online ahead of print. Trends Psychiatry Psychother. 2024. PMID: 38219212 Free PMC article.
-
Examining the role of EGR1 during viral infections.Front Microbiol. 2022 Oct 21;13:1020220. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1020220. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36338037 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berk M., Kapczinski F., Andreazza A. C., Dean O. M., Giorlando F., Maes M., et al. . (2011). Pathways underlying neuroprogression in bipolar disorder: focus on inflammation, oxidative stress and neurotrophic factors. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 35, 804–817. 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2010.10.001 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

