Traversing the Links between Heavy Metal Stress and Plant Signaling
- PMID: 29459874
- PMCID: PMC5807407
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00012
Traversing the Links between Heavy Metal Stress and Plant Signaling
Abstract
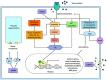
Plants confront multifarious environmental stresses widely divided into abiotic and biotic stresses, of which heavy metal stress represents one of the most damaging abiotic stresses. Heavy metals cause toxicity by targeting crucial molecules and vital processes in the plant cell. One of the approaches by which heavy metals act in plants is by over production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) either directly or indirectly. Plants act against such overdose of metal in the environment by boosting the defense responses like metal chelation, sequestration into vacuole, regulation of metal intake by transporters, and intensification of antioxidative mechanisms. This response shown by plants is the result of intricate signaling networks functioning in the cell in order to transmit the extracellular stimuli into an intracellular response. The crucial signaling components involved are calcium signaling, hormone signaling, and mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling that are discussed in this review. Apart from signaling components other regulators like microRNAs and transcription factors also have a major contribution in regulating heavy metal stress. This review demonstrates the key role of MAPKs in synchronously controlling the other signaling components and regulators in metal stress. Further, attempts have been made to focus on metal transporters and chelators that are regulated by MAPK signaling.
Keywords: MAPKs; calcium signaling; chelators; heavy metals; hormones; metal transporters; metallothioneins; microRNAs.
Figures


References
-
- Ahmad A., Hadi F., Ali N. (2015). Effective phytoextraction of cadmium (Cd) with increasing concentration of total phenolics and free proline in Cannabis sativa (L) plant under various treatments of fertilizers, plant growth regulators and sodium salt. Int. J. Phytoremed. 17, 56–65. 10.1080/15226514.2013.828018 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Al-Hakimi A. M. A. (2007). Modification of cadmium toxicity in pea seedlings by kinetin. Plant Soil Environ. 53, 129–135. 10.4236/ajps.2016.712153 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

