Circulatory white spot syndrome virus in South-West region of Bangladesh from 2014 to 2017: molecular characterization and genetic variation
- PMID: 29460184
- PMCID: PMC5818386
- DOI: 10.1186/s13568-018-0553-z
Circulatory white spot syndrome virus in South-West region of Bangladesh from 2014 to 2017: molecular characterization and genetic variation
Abstract
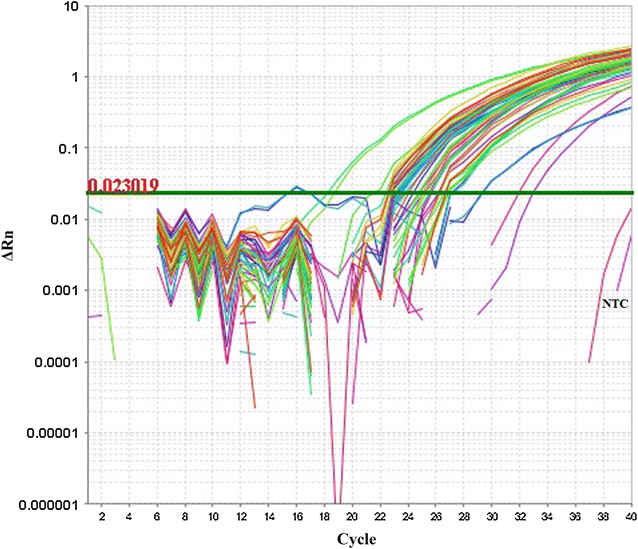
White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV), the etiological agent of White Spot Disease (WSD) is a major impediment for shrimp aquaculture in the worldwide. A critical threshold level of WSSV load in infected shrimp is an important trait for disease manifestation and WSSV transmission in cultured shrimp and subsequently make outbreaks. The present study investigated 120 naturally infected cultured shrimp samples by SYBR Green based qPCR assay for WSD diagnosis and quantification of WSSV load. Among them, 94 samples resulted a variable count of WSSV load ranging from 2.1 × 108 to 2.64 × 1014 copies/g of shrimp tissue. The severity of WSSV infection was assessed based on the established critical threshold load of WSSV in shrimp tissue. Compared to the established critical threshold value of WSSV load in shrimp tissue, our findings showed the horrifying scenario of the severity of WSSV infection in cultured shrimps of Bangladesh that was found to be above the critical limit to initiate an outbreak in the Bangladeshi shrimp aquaculture industry. The latest phylogenetic pattern was altered from the former monophyletic history among WSSVs of Bangladesh due to a variation at 500th nucleotide of VP28 coding gene. Viruses characterized from recent outbreaks in 2015 and 2017 displayed amino acid substitution at position 167 (G→E) on the surface of VP28 protein which has demonstrated the probable replacement of indigenous virus pool. Therefore, it is imperative to take initiative for the management and prevention of WSSV outbreak to sustain shrimp aquaculture in South-West region of Bangladesh.
Keywords: Cultured shrimp; Mutation; Phylogeny; Real-time qPCR; Severity; VP28.
Figures


References
-
- Akaike H (1973) Information theory and an extension of the maximum likelihood principle. In: Petrov BN, Csaki F (eds) Proceedings of the 2nd international symposium on information theory. Akademiai Kiado, Budapest, pp 267–281
-
- Balasubramanian G, Sarathi M, Venkatesan C, Thomas J, Sahul Hameed A. Oral administration of antiviral plant extract of Cynodon dactylon on a large scale production against white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) in Penaeus monodon. Aquaculture. 2008;279:2–5. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2008.03.052. - DOI
-
- BBS, Yearbook of Agricultural Statistics-2017 (28thSeries) Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics, Statistics and Informatics Division (SID), Ministry of Planning, Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh. Dhaka: BBS; 2017.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

