Towards an analytic solution for pulsed CEST
- PMID: 29460973
- PMCID: PMC5935132
- DOI: 10.1002/nbm.3903
Towards an analytic solution for pulsed CEST
Abstract
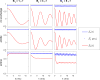
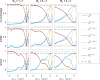
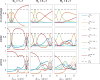
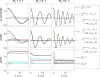
Chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) is an imaging method based on magnetization exchange between solutes and water. This exchange generates changes in the measured signal after off-resonance radiofrequency irradiation. Although the analytic solution for CEST with continuous wave (CW) irradiation has been determined, most studies are performed using pulsed irradiation. In this work, we derive an analytic solution for the CEST signal after pulsed irradiation that includes both short-time rotation effects and long-time saturation effects in a two-pool system corresponding to water and a low-concentration exchanging solute pool. Several approximations are made to balance the accuracy and simplicity of the resulting analytic form, which is tested against numerical solutions of the coupled Bloch equations and is found to be largely accurate for amides at high fields, but less accurate at the higher exchange rates, lower offsets and typically higher irradiation powers of amines.
Keywords: CERT; CEST; analytic; exchange.
Copyright © 2018 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Zhou J, Lal B, Wilson DA, Laterra J, van Zijl PCM. Amide proton transfer (APT) contrast for imaging of brain tumors. Magn Reson Med. 2003;50:1120–1126. - PubMed
-
- Zhou J, Payen J-F, Wilson DA, Traystman RJ, van Zijl PCM. Using the amide proton signals of intracellular proteins and peptides to detect pH effects in MRI. Nat Med. 2003;9:1085–1090. - PubMed
-
- Zaiss M, Bachert P. Exchange-dependent relaxation in the rotating frame for slow and intermediate exchange – modeling off-resonant spin-lock and chemical exchange saturation transfer. NMR Biomed. 2013;26:507–518. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

