Glucose, lipids and gamma-glutamyl transferase measured before prostate cancer diagnosis and secondly diagnosed primary tumours: a prospective study in the Swedish AMORIS cohort
- PMID: 29463235
- PMCID: PMC5819686
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-018-4111-5
Glucose, lipids and gamma-glutamyl transferase measured before prostate cancer diagnosis and secondly diagnosed primary tumours: a prospective study in the Swedish AMORIS cohort
Abstract
Background: Improvements in detection and treatment of prostate cancer (PCa) translate into more men living with PCa, who are therefore potentially at risk of a secondly diagnosed primary tumour (SDPTs). Little is known about potential biochemical mechanisms linking PCa with the occurrence of SDPTs. The current study aims to investigate serum biomarkers of glucose and lipid metabolism and gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) measured prior to PCa diagnosis and their association with the occurrence of SDPTS.
Methods: From the Swedish AMORIS cohort, we selected all men diagnosed with PCa between 1996 and 2011, with at least one of the five biomarkers of interest (glucose, fructosamine, triglycerides, total cholesterol (TC), GGT) measured on average 16 years before PCa diagnosis (n = 10,791). Multivariate Cox proportional hazards models were used to determine hazard ratios (HR) for risk of SDPTs (overall and subtypes) by levels of the five biomarkers. Effect modification of treatment was assessed.
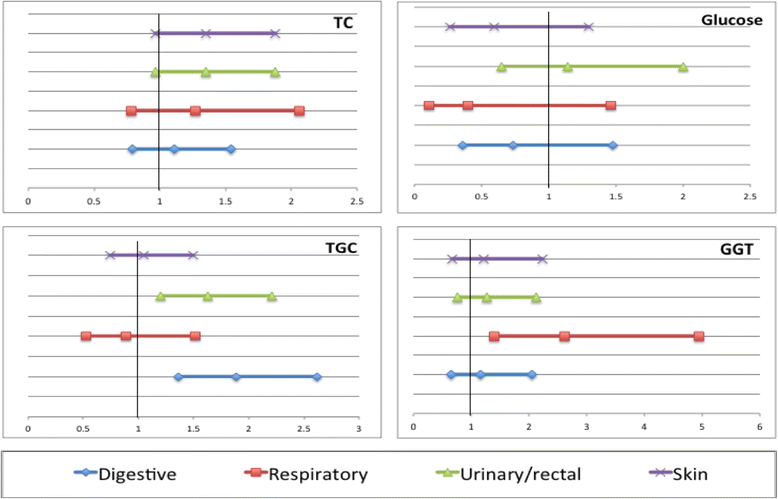
Results: 811 SDPTS were diagnosed during a median follow-up time of 5 years. Elevated levels of triglycerides (HR: 1.37, 95%CI: 1.17-1.60), TC (HR: 1.22, 95%CI: 1.04-1.42) and GGT (HR: 1.32, 95%CI: 1.02-1.71) were associated with an increased risk of SDPTs. Risk of SDPTs subtypes varied by biomarkers.
Conclusion: Elevated levels of biomarkers of lipid metabolism and GGT measured prior to PCa diagnosis were associated with an increased risk of SDPTs, suggesting a potential common biochemical background for development of PCa and SDPTs.
Keywords: Gamma-glutamyl transferase; Glucose; Prostate cancer; Second primary tumours; Total cholesterol; Triglycerides.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study complied with the Declaration of Helsinki, and the ethics review board of the Karolinska Institute approved the study (diary number: 2010/1047–31/1). As with all national register data studies in Sweden, the need for consent has been waived by the ethics review board of the Karolinska Institute.
Consent for publication
NA.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Berrington de Gonzalez A, Curtis RE, Kry SF, Gilbert E, Lamart S, Berg CD, Stovall M, Ron E. Proportion of second cancers attributable to radiotherapy treatment in adults: a cohort study in the US SEER cancer registries. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12(4):353–360. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70061-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

