Fatty acids modulate the expression levels of key proteins for cholesterol absorption in Caco-2 monolayer
- PMID: 29463265
- PMCID: PMC5819267
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-018-0675-y
Fatty acids modulate the expression levels of key proteins for cholesterol absorption in Caco-2 monolayer
Abstract
Background: Fatty acids have been shown to modulate intestinal cholesterol absorption in cells and animals, a process that is mediated by several transporter proteins. Of these proteins, Niemann-Pick C1-Like 1 (NPC1L1) is a major contributor to this process. The current study investigates the unknown mechanism by which fatty acids modulate cholesterol absorption.
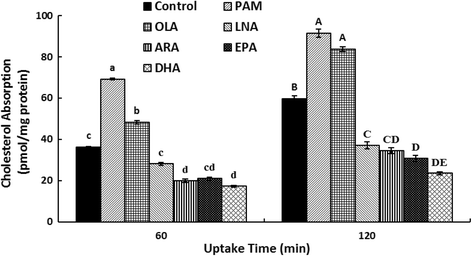
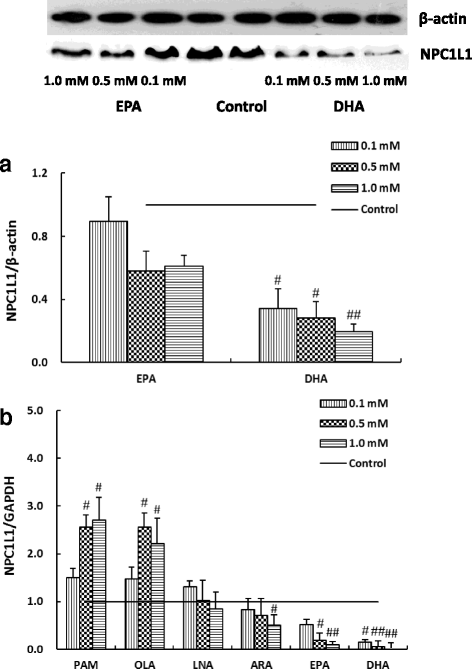
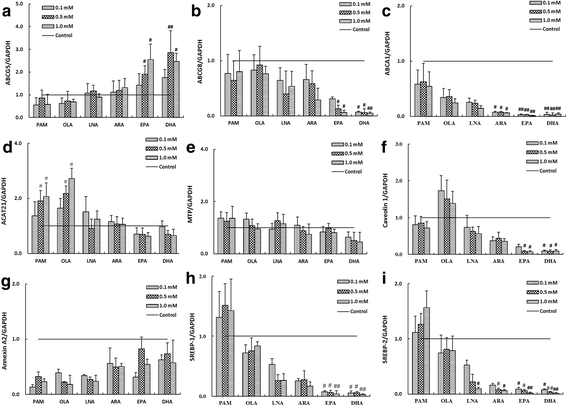
Methods: We evaluated the effects of six fatty acids palmitic acid (PAM), oleic acid (OLA), linoleic acid (LNA), arachidonic acid (ARA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) on cholesterol uptake and transport in human enterocytes Caco-2 cells, and on the mRNA expression levels of NPC1L1, others proteins (ABCG5, ABCG8, ABCA1, ACAT2, MTP, Caveolin 1, Annexin-2) involved in cholesterol absorption, and SREBP-1 and SREBP-2 that are responsible for lipid metabolism.
Results: The polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), especially for EPA and DHA, dose-dependently inhibited cholesterol uptake and transport in Caco-2 monolayer, while saturated fatty acids (SFAs) and monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) had no inhibitory effects. EPA and DHA inhibited cholesterol absorption in Caco-2 monolayer might be caused by down-regulating NPC1L1 mRNA and protein levels, which were associated with inhibition of SREBP-1/- 2 mRNA expression levels.
Conclusion: Results from this study indicate that functional food containing high PUFAs may have potential therapeutic benefit to reduce cholesterol absorption. Further studies on this topic may provide approaches to control lipid metabolism and to promote health.
Keywords: Caco-2 monolayer transport; Fatty acids; Intestinal cholesterol absorption; NPC1L1.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
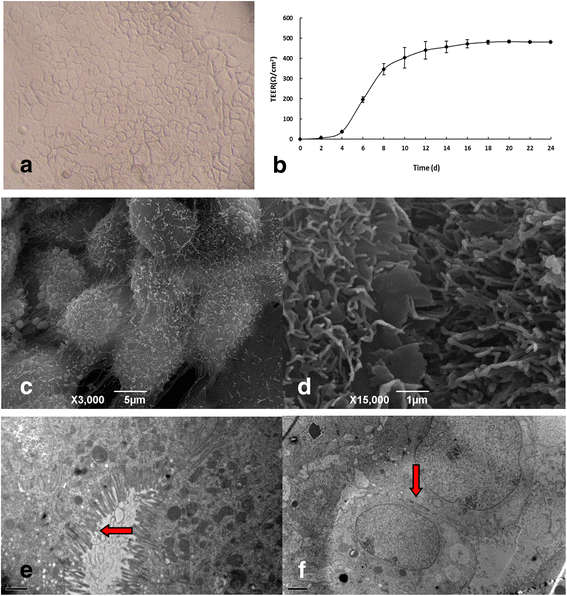
References
-
- National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (adult treatment panel III). Third report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (adult treatment panel III) final report. Circulation. 2002;106(25):3143-3121. - PubMed
-
- Rivellese AA, Maffettone A, Vessby B, Uusitupa M, Hermansen K, Berglund L, et al. Effects of dietary saturated, monounsaturated and n-3 fatty acids on fasting lipoproteins, LDL size and post-prandial lipid metabolism in healthy subjects. Atherosclerosis. 2003;167:149–158. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9150(02)00424-0. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

