Structure of full-length human TRPM4
- PMID: 29463718
- PMCID: PMC5877947
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1722038115
Structure of full-length human TRPM4
Abstract
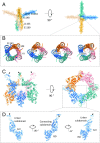
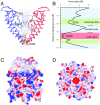
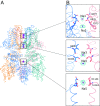
Transient receptor potential melastatin subfamily member 4 (TRPM4) is a widely distributed, calcium-activated, monovalent-selective cation channel. Mutations in human TRPM4 (hTRPM4) result in progressive familial heart block. Here, we report the electron cryomicroscopy structure of hTRPM4 in a closed, Na+-bound, apo state at pH 7.5 to an overall resolution of 3.7 Å. Five partially hydrated sodium ions are proposed to occupy the center of the conduction pore and the entrance to the coiled-coil domain. We identify an upper gate in the selectivity filter and a lower gate at the entrance to the cytoplasmic coiled-coil domain. Intramolecular interactions exist between the TRP domain and the S4-S5 linker, N-terminal domain, and N and C termini. Finally, we identify aromatic interactions via π-π bonds and cation-π bonds, glycosylation at an N-linked extracellular site, a pore-loop disulfide bond, and 24 lipid binding sites. We compare and contrast this structure with other TRP channels and discuss potential mechanisms of regulation and gating of human full-length TRPM4.
Keywords: cardiac arrhythmia; cryomicroscopy; ion channel; transient receptor potential channel.
Copyright © 2018 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


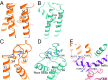
References
-
- Clapham DE, Runnels LW, Strübing C. The TRP ion channel family. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2:387–396. - PubMed
-
- Launay P, et al. TRPM4 is a Ca2+-activated nonselective cation channel mediating cell membrane depolarization. Cell. 2002;109:397–407. - PubMed
-
- Nilius B, et al. The selectivity filter of the cation channel TRPM4. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:22899–22906. - PubMed
-
- Nilius B, et al. Voltage dependence of the Ca2+-activated cation channel TRPM4. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:30813–30820. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

